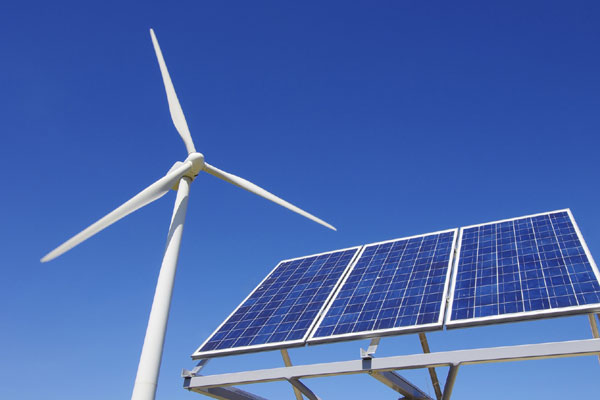
Driven mainly by renewable energies, worldwide capital investment devoted to generation capacity additions is expected to reach $2.2 trillion for the period 2017 to 2021, growth partnership firm Frost & Sullivan said in a new report.
The recent analysis titled “Global Power Industry Outlook, 2018” reveals that a combination of factors led by renewables is set to transform the current power landscape. Increased battery energy storage capabilities, surges in merger and acquisition activities, and the advent of disruptive energy start-ups are contributing to tremendous growth and transformation in the sector.
In early 2017, global solar photovoltaics (PV) capacity surpassed nuclear capacity, driven by high investment levels. The analysis indicates that this growth will continue through 2020 as solar PV is likely to surpass wind capacity, making solar the fourth largest generation type followed by coal, gas and hydro.
The outlook also covers investment and capacity trends for all major generation types through 2021, while also highlighting innovations, challenges facing the industry, and leadership thought points.
“To navigate through current trends and challenges, organizations must start embracing business models that enhance operational and process efficiency while reducing costs. Adopting disruptive digital solutions that focus on consumer needs will bring the organization closer to technological and efficiency transformation,” said Vasanth Krishnan, Energy & Environment analyst at Frost & Sullivan.
Chief highlights and growth opportunities include:
•The 3D’s of Power – Decarbonization, Decentralization, Digitalization – continue to be underlying factors determining the global power market landscape;
•The residential battery storage market will be the fastest growing in 2018 driven largely by the surge in the behind-the-meter residential deployments in the US, Germany, and Australia;
•Over $400 billion will be invested annually in generation capacity additions for the period 2017 to 2021 driven mainly by renewable energies, solar and wind, accounting for $603.4 billion and $553.7 billion, respectively during this period;
•The energy transition is proving to be costly for other sources of generation, and there is little evidence of an improvement in the short term;
•Considering merger and acquisitions strategies to generate necessary funding to invest in new technologies and offerings;
•Futuristic thinking as a necessity - implications of macro changes - renewable energy and electric vehicles are still blurred on the electricity system and decisions must be made in light of these changes.
“Analyzing long-term scenarios and defining positioning strategies should be key focus areas for industry participants in the long term,” noted Krishnan.
“Also, as the renewable and distributed energy markets mature, a large installed capacity of equipment will need to be serviced, offering attractive growth prospects within the operations and maintenance sector,” he added.-TradeArabia News Service