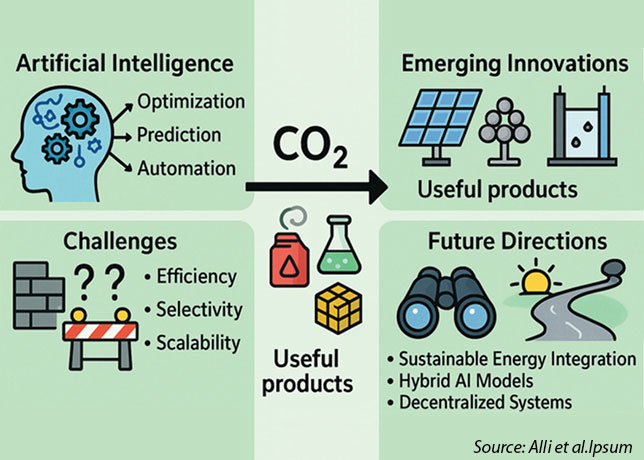
Solar Turbines has a comprehensive portfolio of gas turbines
Solar Turbines has a comprehensive portfolio of gas turbines
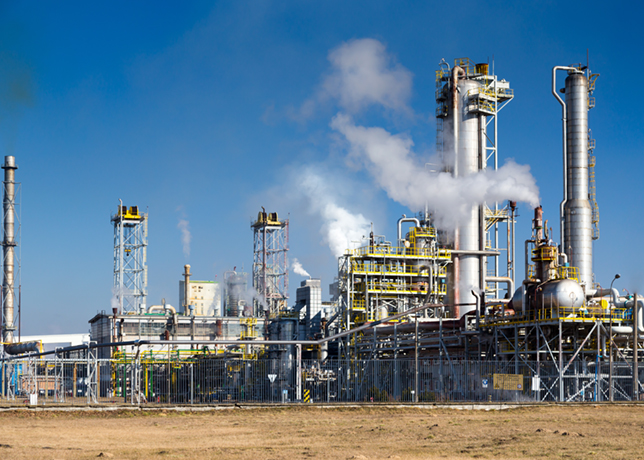
SOLAR Turbines is a manufacturer of industrial gas turbines. The company offers gas turbine engines, gas compressors, gas turbine-powered compressor sets, mechanical-drive packages and generator sets.
A leading market position, comprehensive product portfolio, and synergies with parent company are the major strengths of the company. Though the company has risks associated with competition and stringent regulatory environment, its research and development (R&D) activities and global gas turbine market could offer ample growth opportunities, says GlobalData in a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis of the company.
STRENGTHS
Comprehensive product portfolio: Solar Turbines leverages its comprehensive portfolio of industrial gas turbines and related services for its revenue growth and profitability. The company designs, produces, and distributes gas turbine engines, gas turbine-powered compressor sets, gas compressors, mechanical-drive packages, and generator sets for the production, processing, and pipeline transmission of natural gas and crude oil; and generation of electricity and thermal energy.
It has six gas turbine product families, namely, Saturn, Taurus, Centaur, Mercury, Mars and Titan, and centrifugal gas compressor product families, which include pipeline and production compressors. It manufactures turbines of 1.1 to 22.4 MW capacities with 1,590 to 30,000 horsepower, and it has over 14,500 operating units. The company’s products are certified by Det Norske Veritas and it manufactures them using state-of-the-art operations, which are regularly audited to conform to the ISO 9001 Quality Systems Standard.
The company tests its products thoroughly to verify product quality and performance, and refines and improves them utilising Lean 6 Sigma and proven new product introduction methodologies. The company could leverage its portfolio to enhance its financial and operational position.
Leading market position: The company leverages a strong market position in industrial gas turbines market with an extensive product portfolio and a wide geographical presence. Solar Turbines is one of the leading industrial gas turbine manufacturers in the world.
As of December 31, 2012, the company had market share of 8 per cent globally. It is one of the 50 largest exporters in the US. It exports more than 70 per cent of its products. The company’s offerings find their applications in the development of oil, natural gas and power generation projects in 100 countries worldwide.
The company’s power generation products find their applications in various facilities including industrial/processing facilities, hospitals, colleges and universities, commercial buildings, government facilities, rural and electric cooperatives, and mobile or distributed power plants.
The company has a strong geographical presence across Angola, Argentina, Canada, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, China, India, Denmark, Indonesia, Ireland, Japan, Mexico, Malaysia, Nigeria, Venezuela, the UK, the US, the UAE, Switzerland, Singapore and Russia, among others. Such a strong presence helps the company reach a wide customer base and derive high revenue.
Synergies with parent: Support from its parent company benefits Solar Turbines with exposure and growth. Solar Turbines is one of the leading industrial gas turbine manufacturers in the world.
The company is a part of Caterpillar, a manufacturer of construction and mining equipment, diesel and natural gas engines, industrial gas turbines and diesel-electric locomotives.
It offers its products and services through two businesses divisions: Machinery and Power Systems and Financial Products. Its machinery and power systems business designs, manufactures, markets, and sells construction, mining, and forestry machinery, engines and related products.
Its financial products division offers retail and wholesale financing plans such as operating and finance leases, installment sale contracts, working capital loans and wholesale financing plans to customers and dealers for the purchase and lease of equipment. It also offers remanufacturing and progress rail services.
The company markets and sells its products in several countries across North America, Asia-Pacific, EAME, and Latin America.
Solar Turbines receives considerable benefit from its parent company, Caterpillar in the fields of research and development, technical expertise, manufacturing capabilities, sales and distribution network, and business strategies.
WEAKNESSES
Reliance on third party suppliers: Solar Turbines’s ability to manufacture products is dependent on the availability of certain raw materials and supplies. The company purchases various materials, components and equipment from third party suppliers for its manufacturing operations. The availability of these raw materials and supplies is subject to market forces, which are beyond the control of the company. The company needs to obtain supplies of good quality at a competitive price on a timely basis to meet the demand in the market.
The unavailability of sufficient quantities of raw materials may impact the production of the company. The costs to obtain these raw materials and supplies are subject to price fluctuations. Some of the raw materials or supplies may be subject to regulatory actions, which could affect their availability. Reduced supply and higher prices of raw materials could hamper business, operating results and financial condition.
OPPORTUNITIES
Growth markets for gas turbines: According to the in-house research, average annual global gas turbine revenue stood at $12.3 billion during the 2006-2012 period and is expected to stay nearly stable during the 2013-2020 period. The need for cleaner, more efficient and more reliable natural resources is increasing in line with demand for electricity and rising environmental concerns. Over the historic period 2006-2012, the 200-400 Megawatt (MW) segment of the gas turbine market accounted for the largest share of total market revenue, with average annual revenues of $5.1 billion.
However, over the forecast period, the 120–200 MW segment is predicted to supersede the 200-400 MW segment and contribute the most to the market. Emerging economies in the CIS and the Mena region are prospective markets for gas turbine manufacturers.
Over the 2011–2020 period, electricity generation in CIS member countries is expected to grow at an average of 2 per cent per year, from 1,470 Terawatt hours (TWh) to 1,800 TWh. Gas turbines are expected to play a major role in meeting the electricity demand in the presence of increasing environmental concerns. In 2010, gas turbine power plants accounted for 30 GW of the total installed capacity of 370 GW in CIS countries. By 2020, this is expected to reach 100 GW.
Electricity demand is rising as a result of economic growth and the privatisation and diversification of energy sources. This is also driving the gas turbine market in the Mena region, where sales of gas turbines are expected to surpass sales of steam turbines over the forecast period.
Additionally, electricity demand is predicted to increase by 8–9 per cent annually in countries such as Oman, Qatar, Iraq, and the UAE.
The company could benefit from such growth markets.
Robust R&D activities: Solar Turbines has robust R&D capabilities. The R&D activities of the company focus on improving the performance of products and developing new technologies. The company focuses on R&D activities to develop industrial gas turbines, and enhance and maintain its technological advantages.
Its R&D capabilities enable the company to overcome technical barriers encountered the development of gas turbine engines, gas compressors, gas turbine-powered compressor sets, mechanical-drive packages and generator sets.
The company’s proprietary InSight System technology provides on-line approach to equipment health management, including advanced remote web-based monitoring and predictive diagnostics capabilities.
The company undertook several projects to enhance and develop various products and technologies. Strong R&D capabilities of the company enable it to implement innovative technologies and deliver advanced products and services that meet its customers’ critical needs.
THREATS
Competition: The industries in which the company operates are characterised by huge competition. The company could be subject to intense competitive pressure from various public limited and private companies. Its major competitors include GE, Alstom, Rolls Royce, Siemens and Dresser-Rand.
The company is highly exposed to consumer-related markets, which affect its profitability due to growing pressure on price and demand from customers.
Apart from the established players in the developed countries, players from emerging countries too are competing hard to garner the highest market share. Since many of its competitors have a longer operating history, greater brand recognition, established customer and supplier relationships and greater financial resources, it becomes difficult for the company to compete with them.
Evolving technological environment: The company’s operations undergo rapid and significant changes due to the introduction of innovative technologies.
Solar Turbines operates in a rapidly changing technological environment, and to compete successfully, it should continually develop, manufacture and market innovative products that achieve market acceptance.
Hence, in order to meet its customers’ demands, the company must continuously design new, and update existing products and invest and develop new technologies. The launch of new products and technologies by the company involves a significant commitment to its R&D.
The company strives to develop new technologies. Upon investing in these new technologies, the company’s sales and profits may suffer if they are not accepted in the marketplace as anticipated. At the same time, its competitors may develop advanced products faster than the company, which would adversely affect its competitive position.
Stringent regulatory environment: Solar Turbines has operations globally and faces risks from the protectionist trade policies and changes in the political and regulatory environment such as foreign exchange import and export controls, tariffs and other trade barriers and price or exchange controls.
This could affect the company’s business in several markets, impact the sales and profitability, make the repatriation of profits difficult, expose it to penalties and sanctions, and damage the company’s reputation.
For example, the company conducts business with customers in countries that are subject to export control regulations, embargos, sanctions or other forms of trade restrictions imposed by the US, the European Union or other countries or organisations.
New or tightened export control regulations, sanctions, or other forms of trade restrictions imposed on Iran could result in the curtailment of existing business and a change in its policies.