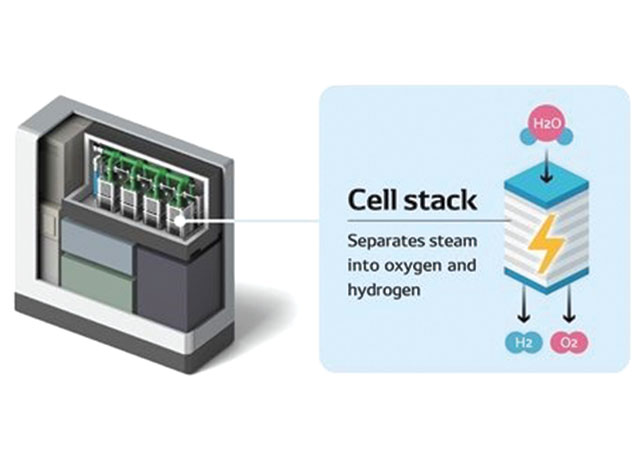
 Cell stacks help separate steam into hydrogen and oxygen
Cell stacks help separate steam into hydrogen and oxygen
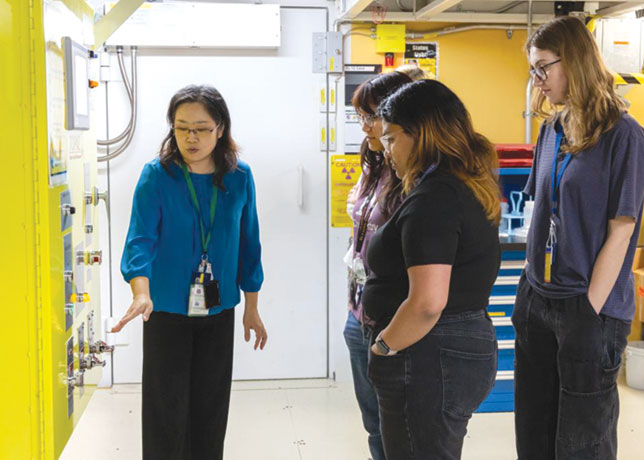
Denso Corporation has signed a manufacturing licence agreement with Ceres Power, a leading developer of solid oxide cell stack technology. Denso aims to advance the early practical application of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOECs) that produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
Cell stacks are one of the components of SOECs, playing a role in separating steam into hydrogen and oxygen.
Ceres has unique solid oxide technology joining metal and ceramic that leads to high-output performance.
Denso aims to mass producte high-quality cell stacks by utilising Ceres’ technology with the company’s expertise of ceramic technology it has built in the automotive field, and to achieve the early practical application of SOECs with the company’s system technology including thermal management, system control and so forth.
Hydrogen is one of the leading next-generation energy sources to realise a carbon-neutral society, and its technology development is selected depending on the location, scale and application.
Denso will continue to promote various development of hydrogen utilisation technologies through collaboration with partners both domestically and internationally, contributing to the creation of a carbon-neutral society.