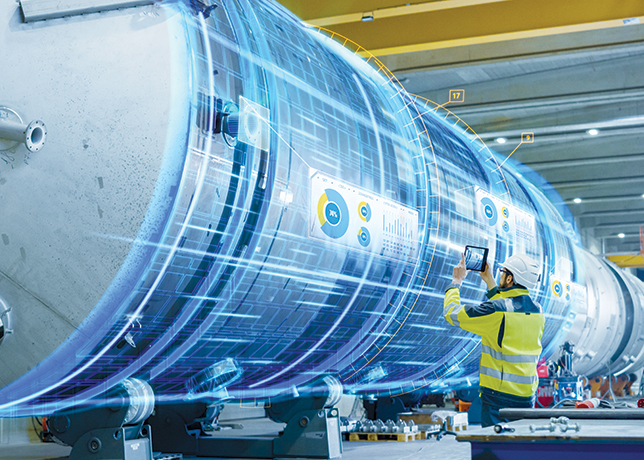
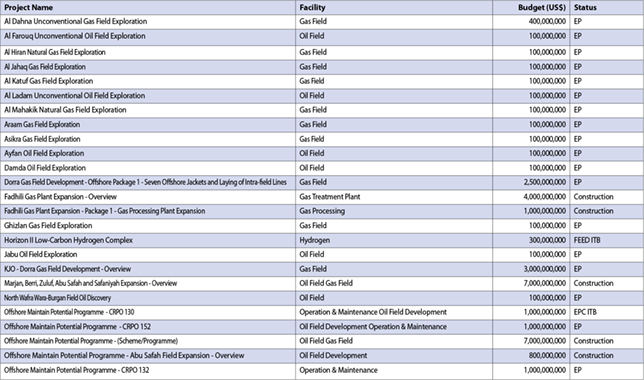
IoT technologies help the energy industry to boost asset utilisation and efficiency
IoT technologies help the energy industry to boost asset utilisation and efficiency
IoT technologies boost efficiency, safety, and sustainability in oil and gas, driving rapid market growth while overcoming challenges like harsh environments and cybersecurity risks
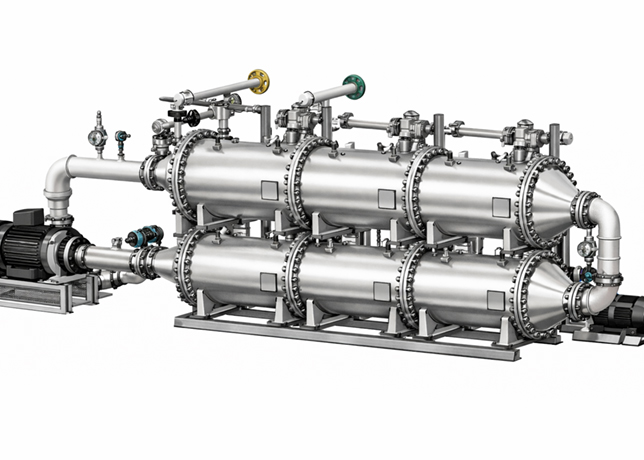
The oil and gas industry is undergoing a significant transformation, with the Internet of Things (IoT) playing a key role in driving operational efficiency, safety, and cost reduction.
By enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven insights, IoT technologies are reshaping how companies manage their assets and processes.
The global IoT market in oil and gas is expected to grow rapidly, reaching $9.3 billion by 2034 from $2.5 billion in 2024, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.10 per cent.
In an industry where unplanned downtime due to equipment failure can be costly, IoT is proving invaluable.
By using connected sensors, businesses can remotely monitor assets, predict maintenance needs, and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
This proactive approach reduces downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and extends asset lifespans.
Furthermore, IoT technologies improve safety by tracking environmental conditions such as gas leaks, seismic activity, and air quality, allowing for early warnings and rapid responses to potential hazards.
One of IoT's major benefits is predictive maintenance. Unlike traditional time-based maintenance, which follows set schedules, IoT-enabled predictive maintenance uses real-time data to assess equipment health and schedule repairs as needed.
By monitoring factors like temperature, vibration, and pressure, IoT detects potential issues before they lead to equipment failure, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
IoT also boosts asset utilisation and productivity. Digital twins–virtual replicas of physical assets–allow companies to simulate real-world conditions and optimise operations without risking damage to actual equipment.
This data-driven approach enables better decision-making, helping businesses improve production strategies and operational performance.
Environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance are other areas where IoT makes a significant impact.
By monitoring air quality, water usage, and emissions, IoT helps companies reduce their environmental footprint and adhere to industry regulations.
IoT also enables resource optimisation, such as improving energy and water efficiency, which in turn lowers operational costs.
Across the oil and gas value chain, IoT applications are transforming operations. In pipeline monitoring, IoT devices detect leaks and send alerts, preventing disasters and minimising environmental impact.
Smart pumping systems, powered by IoT, optimise energy consumption, reducing operating costs while ensuring peak efficiency.
In drilling operations, IoT devices collect and transmit data on key parameters like drilling conditions, equipment status, and geophysical factors.
This real-time information allows operators to make immediate adjustments, enhancing efficiency and reducing the risk of costly failures.
Digital twins in drilling operations help optimise strategies by simulating various scenarios without physical trials, leading to more effective and cost-efficient drilling.
Refining and processing operations also benefit from IoT. By embedding sensors throughout refining systems, companies can monitor critical variables like temperature, pressure, and flow rates in real-time.
This data allows for more precise control, reducing errors and improving production efficiency. IoT technologies streamline the refining process, reducing the need for manual labour and optimising operations for greater efficiency.
CHALLENGES
Implementing IoT in the oil and gas industry comes with challenges. One major concern is the harsh operating environments in which many oil and gas operations take place.
To address these challenges, companies must invest in industrial-grade IoT solutions specifically designed to withstand these harsh conditions.
Connectivity is another obstacle, particularly in remote offshore platforms and pipelines where reliable internet access can be limited.
A hybrid connectivity approach that combines satellite communication with terrestrial networks can help overcome this, ensuring IoT devices remain connected even in isolated regions.
Cybersecurity is a growing concern as the number of connected devices in the oil and gas sector increases.
Companies must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data from cyber-attacks.
This includes regular vulnerability assessments, strong IT infrastructure, and secure communication protocols to safeguard IoT systems.
Scalability presents another challenge. As IoT systems expand to accommodate more devices, companies must design flexible, scalable architectures that can handle large volumes of connected devices.
Cloud-based solutions can help address scalability issues, offering the necessary flexibility to grow with the business.
Data management is another hurdle. IoT generates vast amounts of data, which can overwhelm traditional systems.
To manage this, businesses can use advanced analytics tools and edge computing, which process data closer to the source and enable more efficient data management.
This approach allows companies to derive meaningful insights from the data, helping them make informed decisions and optimise their operations.
The technology enables companies to monitor and optimise operations in real-time, predict maintenance needs, and reduce costs.
Despite challenges such as harsh environments, connectivity issues, and cybersecurity risks, the benefits of IoT far outweigh the obstacles.
As more companies adopt IoT solutions, the industry will continue to evolve, becoming more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible.
With the right strategies in place, IoT can help oil and gas companies navigate modern challenges and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly complex market.