Oman is driving green hydrogen production for net-zero
Oman is driving green hydrogen production for net-zero
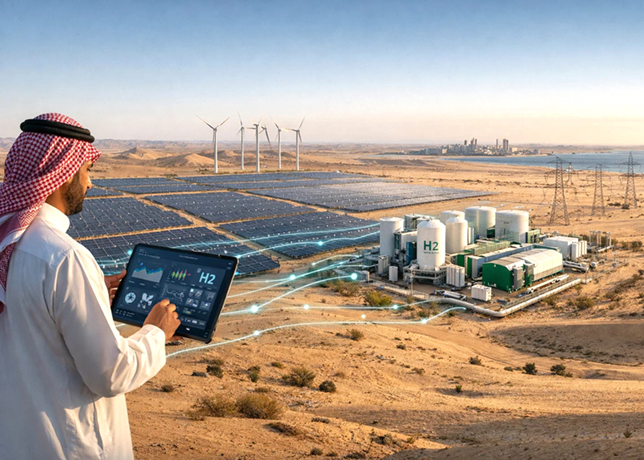
Oman is leading an ambitious green hydrogen strategy, targeting substantial production increases and economic diversification by leveraging its renewable resources, strategic location, and significant investments
Oman is setting a robust example in the global transition to renewable energy with its ambitious green hydrogen strategy.
The country is poised to become a leading global hub for green hydrogen, leveraging its abundant renewable energy resources, strategic geographic location, and clear, actionable plans.
This comprehensive approach aims to diversify the economy, ensure energy security, and contribute significantly to global decarbonisation efforts.
Oman’s Green Hydrogen Strategy delineates a path toward significant contributions to both local and global hydrogen markets.
By 2030, Oman targets an impressive production capacity of 1 to 1.5 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) of green hydrogen, scaling up to 8-15 mtpa by 2040 and eventually reaching 35-40 mtpa by 2050.
These ambitious targets are underpinned by investments exceeding $38 billion, aimed at building infrastructure, developing shared facilities, and ensuring a competitive levelised cost of hydrogen (LCOH) for export markets.
RENEWABLE RESOURCES & INFRASTRUCTURE
 |
The Amin solar park in Oman ... 1,500 sq km of land has been earmarked for green hydrogen |
Oman is endowed with some of the world’s best renewable resources. The country has allocated around 50,000 sq km of land specifically for green hydrogen projects, with regions like Duqm, Sohar, and Dhofar earmarked for extensive renewable energy development.
Wind and solar resources in these areas are exceptionally favorable, with wind speeds up to 11 m per second and solar irradiation exceeding 2,400 kWh/sq m.
To support this vast potential, Oman is developing a comprehensive infrastructure network. This includes the establishment of shared facilities such as electricity transmission lines, water pipelines, and hydrogen transport systems. Hydrom, Oman’s dedicated entity for green hydrogen, plays a pivotal role as the central orchestrator, managing policies, auctions, and the development of this infrastructure.
Oman’s strategy includes a transparent and competitive auction process to allocate land for green hydrogen projects.
The first auction round has already seen significant success, with six projects awarded, positioning Oman as a top contender in the global hydrogen market. These projects are expected to generate around 1.38 mtpa of hydrogen by 2030, supported by an installed renewable capacity of 34.8 GW and investments totaling $49 billion.
The second round of auctions is already in progress, with additional projects being awarded to further bolster Oman’s green hydrogen capabilities.
This competitive process ensures that only the most viable and innovative projects are selected, fostering a robust and efficient green hydrogen sector.
ECONOMIC DIVERSIFICATION & JOB CREATION
One of the core goals of Oman’s green hydrogen strategy is economic diversification. By onshoring the supply chain and developing downstream industries, Oman aims to create long-term, sustainable jobs and reduce its reliance on oil and gas revenues.
The development of a green hydrogen sector is expected to spur growth in related industries such as green steel, ammonia production, and renewable energy technology manufacturing.
 |
The importance of transportation for green hydrogen cannot be overstated |
Oman’s commitment to localisation is evident in its strategy to integrate local content requirements and incentivise domestic sourcing.
This approach not only boosts the local economy but also ensures that the benefits of the green hydrogen transition are widely shared among Omani businesses and citizens.
ENVIRONMENTAL & GLOBAL IMPACT
Oman’s foray into green hydrogen is a critical component of its broader strategy to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
By replacing fossil fuels with green hydrogen in various sectors, Oman can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and contribute to global climate goals.
The hydrogen produced in Oman will primarily cater to export markets in Europe and Asia, regions that are keenly pursuing decarbonisation.
The potential for green hydrogen to transform industries such as transportation, shipping, and heavy manufacturing cannot be overstated.
Hydrogen’s versatility as a clean energy carrier makes it an ideal solution for sectors that are challenging to electrify, thus playing a crucial role in the global energy transition.
Oman recognises the importance of innovation and capability development in achieving its green hydrogen goals.
The country is investing in research and development to enhance the efficiency of hydrogen production technologies and to explore new applications for green hydrogen.
Education and training programmes are being developed to equip the local workforce with the skills needed to operate and maintain advanced hydrogen technologies.
Hydrom’s role extends to coordinating with various stakeholders, including international developers, technology providers, and research institutions.
Hydrom was established in 2022 in response to a directive from His Majesty Haitham bin Tarik, Sultan and Prime Minister of Oman, aimed at structuring and expediting the development of Oman's green hydrogen sector. It is fully owned by Energy Development Oman.
This collaborative approach ensures that Oman stays at the forefront of green hydrogen innovation and can adapt to evolving market and technological trends.
Oman’s green hydrogen strategy is designed to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and foster international partnerships.
The country’s political and economic stability, coupled with its strategic location between Europe and Asia, makes it an attractive destination for global investors.
The transparent auction process and the clear regulatory framework further enhance Oman’s appeal as a reliable partner in the green hydrogen sector.
International companies are encouraged to participate in Oman’s green hydrogen projects, either as developers, financial partners, or technology providers.
These collaborations are expected to bring in advanced technologies, expertise, and capital, driving the rapid development of Oman’s green hydrogen ecosystem.
COMMITMENT TO GREEN HYDROGEN
Oman’s commitment to green hydrogen is a strategic component of its broader vision for economic and environmental sustainability.
Mohsen bin Hamed Al Hadhrami, the Under-Secretary of the Ministry of Energy and Minerals, emphasised the critical need for collective action to address the unprecedented challenges posed by climate change.
Oman has made significant strides in its green hydrogen journey. Over the past year, concepts discussed have matured, leading to the signing of landmark agreements, including one focused on exploring energy storage.
Storage is a vital component for making green hydrogen competitive and viable in the future. Additionally, Oman has signed its sixth green hydrogen project, bringing the total investment in the sector to an impressive $38 billion.
To sustain this momentum, several key factors are essential. First, developing In-Country Value (ICV) is crucial.
Localising activities within the green hydrogen industry ensures sustainability and promotes social responsibility and business viability. Second, securing offtakers for Oman’s green hydrogen output is vital.
This requires collaboration with the global market to ensure that green hydrogen products are delivered reliably, sustainably, and at competitive prices.
PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION
 |
Oman has made a total of $38 billion investments in hydrogen projects |
The practical aspects of implementation are equally important. The manufacturing of equipment such as wind turbines, solar panels, and electrolyser modules needs to begin by 2027-2028.
This necessitates access to resources at scale and readiness from industry, government, and investors. Balancing green energy costs with affordability is a critical challenge.
Collaborative efforts between governments and industries are needed to address inefficiencies, waste, and policy shortcomings.
Technology plays a pivotal role in driving the transition, supported by access to critical minerals.
Oman has been modernising its mineral sector, focusing on digitalisation of data and introducing high standards for health, safety, and environment (HSE).
With the target of producing 1 million tonnes of green hydrogen per year by 2030, Oman faces potential challenges. The simultaneous progress of multiple projects could strain construction capabilities, labor resources, and logistical infrastructure.
To navigate these complexities, the Ministry is creating a dedicated project delivery unit. This unit will anticipate potential hurdles and implement pre-emptive solutions, ensuring adequate transportation infrastructure, skilled labor, and regulatory compliance.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY & MARKET LIBERALISATION
Energy efficiency is a low-hanging fruit that supports the decarbonisation drive. The regulatory framework governing the electricity market is being reviewed to enable greater renewable energy contributions.
The liberalisation of the market will facilitate the integration of renewable energy into the grid, supporting the decarbonisation journey.
Oman is exploring hydrogen production across green, blue, and white hydrogen. Governance structures for green hydrogen are mature, while blue hydrogen is being assessed as part of the CCUS framework.
The country is also exploring carbon capture, utilisation, and sequestration as a pathway in its orderly transition.
To ensure compliance across different energy verticals, Oman is formulating guidelines for certification standards.
This involves collaboration with government entities, private sector elements, and international organisations.
The Oman Sustainability Centre will oversee these efforts once established. Oman anticipates challenges related to supply, demand, and the intricacies of the supply chain.
Market regulations at the import end, such as the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanisms (CBAM), set high standards. Alternatives like a 'book and claim' system could benefit landlocked nations, facilitating decarbonisation.
The Ministry of Energy and Minerals is working on an energy model that considers primary energy resources across Oman.
This model articulates and simulates different scenarios, including the impact of green hydrogen on job creation, the primary energy mix, and total greenhouse gas emissions.
Collaboration with key stakeholders has been crucial in formulating these scenarios. Securing ample land for green hydrogen development is a priority. Oman has obtained 65,000 sq km of solar and wind-rich acreage.
Offshore sites are also being examined for inclusion in renewable energy and green hydrogen projects. Collaboration with other entities, such as the Oman Investment Authority (OIA), supports these efforts.
Hydrom has witnessed significant progress in planning and orchestrating Oman’s green hydrogen industry.
With two successful auction rounds of land blocks completed, Hydrom is also focusing on common infrastructure and localisation opportunities.
The creation of a dedicated entity, provisionally named ‘InfraCo,’ will oversee shared infrastructure, including transportation corridors and utilities. Hydrom is engaging national champions like OQ Gas Networks, Oman Electricity Transmission Company (OETC), and Nama Water Services to support the development of the green hydrogen industry. A three-phase strategy has been outlined to ensure the infrastructure is operational by mid-2029.
LOCALISATION & MANUFACTURING
Oman is keen on localising manufacturing, operations, and maintenance across the green hydrogen ecosystem. This includes potential partnerships with global energy technology giants like Siemens Energy to develop a domestic electrolyser manufacturing facility. Investors are encouraged to establish manufacturing facilities in Oman, leveraging the country’s strategic advantages.
OQ Alternative Energy (AE) is a significant player in Oman’s green hydrogen push, with stakes in three mega projects.
These projects, totaling over 30 GW of renewables, are expected to contribute significantly to Oman’s hydrogen production targets by 2030. The company’s focus is on achieving bankable offtake and addressing transportation challenges for green hydrogen derivatives.
CONCLUSION
Oman’s strategic vision for green hydrogen production reflects a commitment to sustainability and economic growth.
Through collaboration, strategic planning, and leveraging its natural resources, Oman is poised to become a global leader in green hydrogen, driving the transition to a low-carbon future.
As Oman continues to implement its strategy and attract international collaboration, it sets a powerful example of how nations can effectively transition to a green economy while securing long-term economic and environmental benefits.