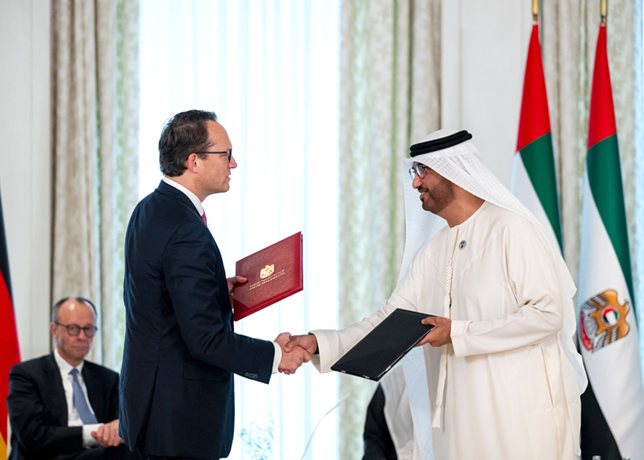
Alvera and Al Jamali (right) sign the agreement in the presence of senior Omani officials
Alvera and Al Jamali (right) sign the agreement in the presence of senior Omani officials
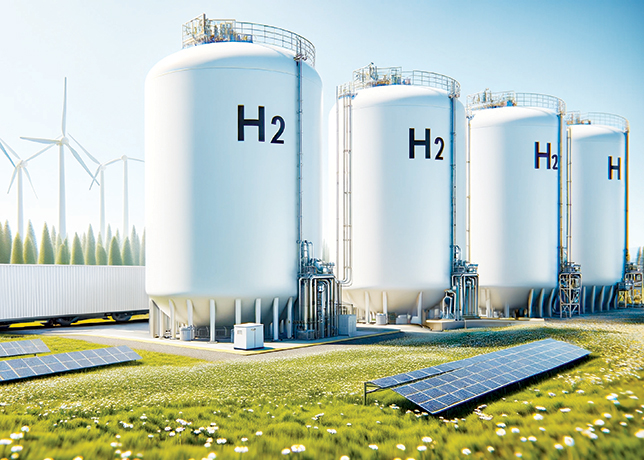
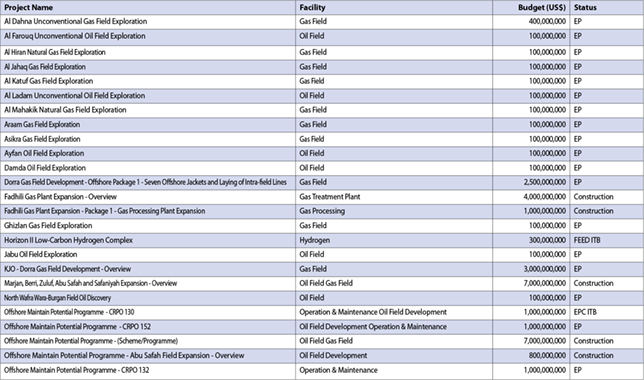
The green hydrogen-based green molecule is chemically identical to natural gas and can be immediately used in the existing gas infrastructure for liquefaction, regasification, transportation and storage Three Energy Solutions (TES) and OQ Alternative Energy have entered a joint study agreement to assess the development of an e-NG (electric natural gas) facility in Oman.
Oman has been at the forefront in the development of a green hydrogen economy where the country aims to produce in excess of 1 million tonnes annum of green hydrogen by 2030.
Its strong renewable resources, in particular wind and solar, combined with a one stop-shop implementation framework under Hydrom’s directive, has been promoting the Sultanate to be amongst the most interesting hubs to produce green hydrogen.
 |
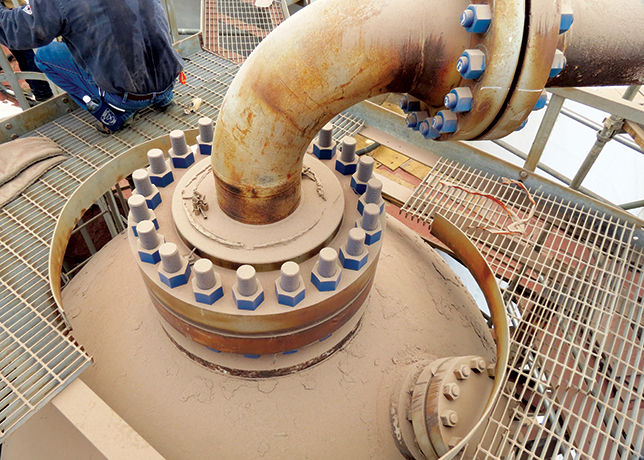
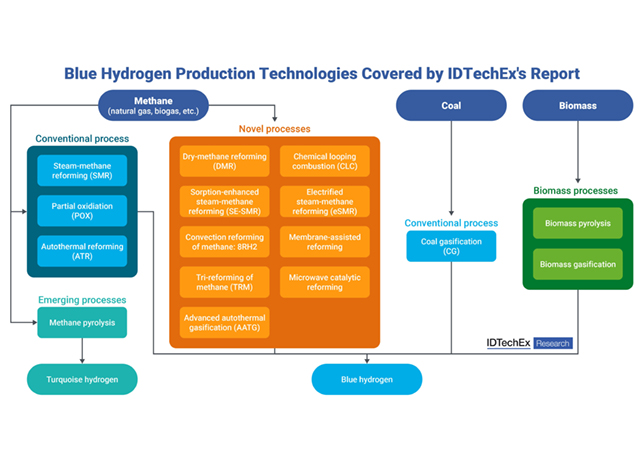
The e-NG making process |
e-NG is a green hydrogen-based green molecule chemically identical to natural gas (on a molecular level) and obtained by combining, through a methanation process (called Sabatier), green H2 with CO2, producing green CH4.
As such, it can immediately be used in the existing gas infrastructure for liquefaction, regasification, transportation and importantly storage and be a drop-in solution for industrial usage gradually replacing natural gas.
'This agreement with OQAE underscores our dedication to advancing the global energy transition and strengthens our commitment and ongoing activities in the Middle East. By harnessing the expertise of OQAE, a global leader in the energy industry, we are enabling the production of green hydrogen at an industrial scale, making e-fuels accessible and cost-effective,' said Marco Alvera, CEO and Co-Founder of TES.
Najla Al Jamali, CEO of OQ Alternative Energy, said: 'At OQ, we are committed to advancing Oman’s energy transition through building partnerships, creating innovative solutions, and implementing sustainable practices. This collaboration marks our dedication to innovation, sustainability, and shaping the future of energy. Collaborating on the study helps us move forward to identify additional downstream opportunities and vectors to diversify markets for green hydrogen.'
Headquartered in Europe, TES is a global green energy company leading the way in the production of e-NG.
The company’s green hydrogen model uses solar and wind energy in low-cost areas with abundant sunlight or wind to create green hydrogen, which is then combined with recycled CO2 from industrial emissions, CO2 from Direct Air Capture and biogenic CO2, to create 'synthetic methane' or 'green gas'.
e-NG is easy to transport and store using existing infrastructure.
By 2030, TES plans to produce about 15 TWh of e-NG annually, equivalent to 0.4 megatons of green hydrogen, thus avoiding CO2 emissions of 2.5 million tons annually by 2030.
TES also co-founded the global e-NG Coalition in March 2024 with industry leaders TotalEnergies, Engie, Sempra Infrastructure, Mitsubishi Corporation, Tokyo Gas, Osaka Gas and Toho Gas.