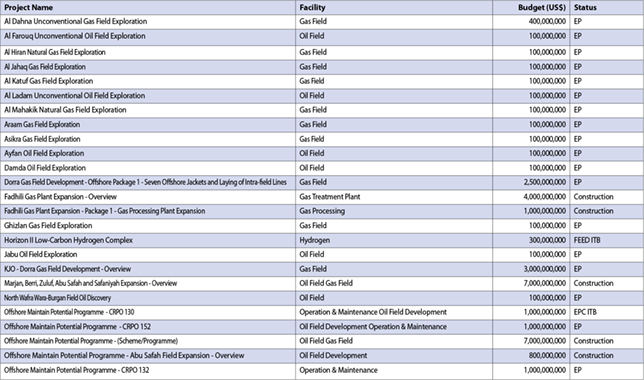
 Ford window made of advanced polycarbondate made by Sabic
Ford window made of advanced polycarbondate made by Sabic
AMONG the technologies Ford incorporated into its drivable multi-material lightweight vehicle (MMLV) is an advanced polycarbonate (PC) glazing solution from Sabic’s Innovative Plastics business that makes possible a 35 per cent weight reduction compared to the same window on a 2013 model year Ford Fusion production vehicle.
The weight savings total 7.4 pounds (3.36 kg), even though the rear window is more than one millimetre thicker than the production glass window it replaces. The PC material has approximately half the density of glass.
The advanced PC solution used in the concept’s rear window combines Lexan resin, a PC material characterised by its light weight, high optical clarity and impact resistance, with Exatec E900 plasma coating for glass-like scratch and UV resistance.
The lightweight concept vehicle was developed with the US Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Programme, together with Cosma International – a subsidiary of Magna International—to illustrate long-term potential light-weighting solutions. Sabic contributed PC glazing materials, advanced coatings technology and engineering design expertise to support the rear window’s development and production.
Lexan polycarbonate resin is an amorphous engineering thermoplastic, characterised by outstanding mechanical, optical, electrical and thermal properties.
The E900 coating, an offering unique to Sabic, is designed to deliver a high level of weatherability and abrasion resistance over the life of the vehicle and enable automakers to meet homologation requirements for driver visibility – including US standards such as the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) 205 regulations, as governed by the NHTSA AS2 specification, and the American National Standards Institute Z26.1, which covers the visibility, strength and abrasion resistance of glazing materials.
Sabic has determined that use of PC glazing can contribute to the sustainability of a vehicle by improving energy efficiency and reducing emissions. This boost in energy efficiency can come not only from weight reduction, but also from improved thermal insulation of the passenger cabin, a result of PC’s five-fold lower thermal conductivity relative to glass.
Sabic’s advanced computer analyses have quantified Lexan resin’s potential to reduce the load on HVAC (heating, ventilating and air conditioning) systems: emissions can be cut by as much as three grams of carbon dioxide per kilometer, and the range of electric and hybrid vehicles can be extended by two to three per cent.
Sabic is committed to spread the adoption of PC glazing technology, which offers styling and weight saving benefits to help increase fuel efficiency and lower emissions. To date, several OEMs have validated the technology for use on rear quarter windows and roofs on production vehicles. At the same time, real-world demonstration programs like Ford’s drivable multi-material lightweight vehicle concept are valuable to further highlight the performance gains that can come from an advanced approach like PC glazing and to ultimately help validate and speed up its wide-scale adoption.
The rear window of Ford’s MMLV is identical in geometry to the part used in the Fusion production vehicle. This design approach allows Ford to test the two parts and compare the performance differences between them based strictly on the change in materials.
The material’s ability to be injection-molded means windows can be designed to reduce even more weight, increase aerodynamic performance and enhance styling. Designs can go beyond the shape and complexity limitations of glass to glazing with geometric effects that can make possible relatively thin PC surfaces, potentially adding to the weight-out total.
Also, 3D styling possibilities and aerodynamic features enabled by PC glazing can minimise drag and contribute to fuel efficiency.
Integration opportunities, enabled by PC glazing, can also contribute to enhanced efficiency – and cost savings – by reducing the number of parts and materials associated with joining otherwise discrete components.
Another consideration for automotive OEMs and suppliers is the maturity of PC glazing technology and its suitability for mass production. In collaboration with ULVAC, a leading global supplier of mass production systems, Sabic has helped develop an advanced vacuum equipment technology for the automotive industry to develop lightweight, plasma-coated PC glazing components cost-effectively and efficiently on a broad scale.
In addition to PC glazing, Sabic offers thermoplastic solutions for almost every major application space on a vehicle. In the 2013 model year Ford Fusion, for example, about 20 kilograms of Sabic resins are used to reduce weight and meet diverse performance requirements for chassis, forward lighting, interior and structural, exterior, electrical and underhood applications.
Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (Sabic) ranks among the world’s top petrochemical companies. The company is among the world’s market leaders in the production of polyethylene, polypropylene and other advanced thermoplastics, glycols, methanol and fertilisers.