Yusuf Bin Ahmed Kanoo ... technological disruption is creating major shifts
Yusuf Bin Ahmed Kanoo ... technological disruption is creating major shifts
Not only will the industry have to reduce emissions, it will also have to think broader while crafting its strategies, consider environmental challenges, and various stakeholders, Ali Kanoo and Manoj Tripathy from the Kanoo Group tell OGN
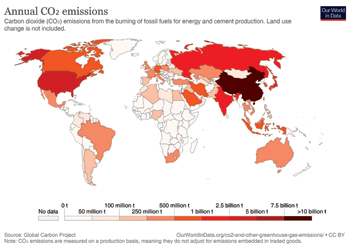
As the world countries pledge to take action against climate change, the energy industry is now under pressure more than ever to decrease carbon emissions.
Technological innovation will play a big role in overcoming the environmental challenges and help the world avoid the catastrophic damage that rising temperatures could pose to humanity.
In an interview with Abdulaziz Khattak of OGN, Ali Abdulla Kanoo, Deputy Chairman of Yusuf Bin Ahmed Kanoo Company, Saudi Arabia, and Manoj Kumar Tripathy, CEO - Kanoo Industrial & Energy Yusuf Bin Ahmed Kanoo Group, tell us how the future of energy will look like, and the challenges the industry faces.
 |
|
Manoj Kumar Tripathy |
What is your take on the global energy market and digital disruption in the sector?
Technology continues to possess the power to disrupt sectors like oil and gas, and energy in general, helping companies by finding operational proficiencies in addition to addressing the growing environmental concerns.
In the coming decades, the energy market will continue to witness disruption due to the popular digital trends like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and data analytics. These technologies have potentially resulted in improved productivity, safety, and sustainability.
The application of advanced technologies across the industry, transforms the nature of businesses and organisations, and requires new skills to address coming opportunities and risks.
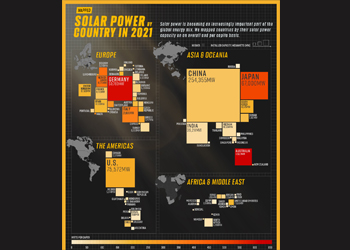
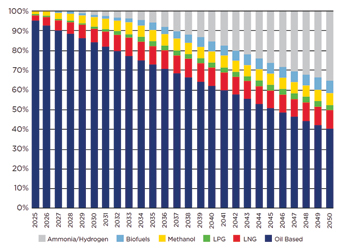
Disruption driven by technological innovation and adoption of clean tech, particularly solar generation, along with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), is creating major shifts.
It is estimated that the cost of solar will drop so much that by 2030 all innovation in energy will involve solar; EVs will gain more popularity and new vehicles will have driverless capabilities; and the energy grid will become an ‘internet of energy’.
The future will enable customers to upload and download energy on the grid, track transactions on apps built and run on blockchain architecture.
Today there are political, regulatory, technological, and economic forces driving the rapid adoption of clean, non-carbon-based alternative energy sources, namely nuclear, solar, hydrogen, etc.
The long-term demand has opened avenues for other environmental conscious technologies, including innovation in biofuels, autonomous vehicles, ride sharing, smart cities and fuel efficiency programmes.
How do you see the UAE’s National Energy Strategy 2050?
The UAE government is committed to bringing a quality change in the culture of energy consumption. It is striving to diversify its sources of energy by enabling the contribution of clean energy and actively reducing energy consumption.
The strategy is focused on increasing the consumption of clean energy from 25-50 per cent, reduce carbon emission resulting from the power generation process by 70 per cent, and improve energy efficiency by 40 per cent by 2050.
The aim to invest Dh600 billion ($163 billion) to meet demands for energy to ensure the sustainability of growth in the UAE’s economy is one of the key objectives.
This strategy will accelerate economic growth and investment in energy storage, contributing to reducing power consumption.
These efforts mark the beginning of the sustainability of the UAE’s power sector and its commitment to achieve carbon neutrality.
These efforts also highlight the UAE leadership’s position in facing climate change by embracing sustainability and using renewable and clean energy technologies.
What are the strategic challenges faced by the energy sector?
Renewable energy has become a mainstream part of the energy industry and with the fast-paced growth, it’s seeking more robust policy structures. Regulators are expected to consider various factors ensuring financially viability for designing future energy systems.
Industries that cannot cut down their carbon emissions will have to face more scrutiny.
Industries will have to think broader while crafting their strategies, consider environmental challenges, and not just shareholders but and various stakeholders.
Energy companies will have to ramp up investment in innovative technologies to address environmental concerns and embrace digital technologies.
The world still lacks safe, low-carbon, and cheap large-scale energy alternatives to fossil fuels. Until we scale up those alternatives, the world will continue to struggle to overcome the challenges of carbon emission.
What are the challenges posed by new emissions targets?
The industry needs to minimise its own emissions – produced from production, processing, and logistics – which contributes approximately 20 per cent to the lifecycle along with 80 per cent emission due to fuel burnt by consumers.
There is an urgent need to address emissions that are released.
The cost of capital rises with the demand of oil increase, and carbon taxes also come into the play. Considering these factors, decarbonisation is indeed the key to retain the support of users and regulators.
Net-zero plans rely on promises of future carbon removal. It might not be practical to compensate for the cumulative emissions if the technologies anticipated to remove huge quantities of carbon in the future fail to work.
What are some of the latest technological innovations to address issues like lower carbon emissions?
With the growing urban areas and smart cities becoming the new reality, greenhouse gas emissions are likely to grow along with them.
The challenge is to ensure that our smart cities become greener while we manage the challenges imposed.
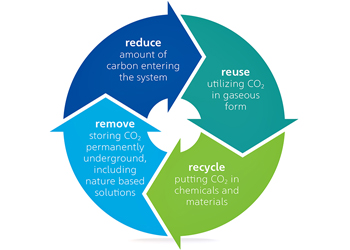
The advancements in renewable energy and EVs have already led to significant reductions in carbon emissions.
Carbon emissions are being reduced by making power on-site with renewables and other climate-friendly energy resources.
Some of the recent innovations like rooftop solar panels, solar water heating, small-scale wind generation, fuel cells powered by natural gas or renewable hydrogen are contributing positively to cope up with the issues of carbon emission.
Can you offer some insights about the new products and solutions in this regard?
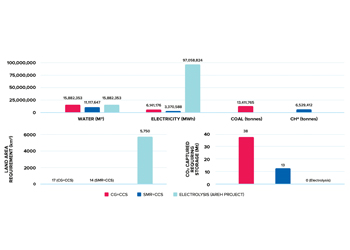
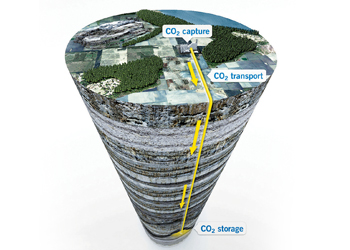
Direct air carbon capture and storage is a new technology that the world has the highest hope from, for removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Since it would allow large amounts of CO2 to be, in effect, trapped, this technology could play a very big role to reduce the greenhouse effect.
What is Kanoo Group’s contribution in building the energy workforce of the future?
Kanoo Group is currently engaged in strategising, investing into new talent, building cooperation with various OEM’s and clients to source new technologies and exchange expertise and know-how, as well as contributing to building national capacities in energy technologies.
This involves investing in renewable energy, gas fired power solutions, the Internet of Things (IoT), using artificial intelligence (AI) in energy production unit, 3D printing and additive manufacturing, etc.




































































-...jpg)