 Lu ... ensuring safety
Lu ... ensuring safety
It is key to ensure the safe operation of the valve while making it more efficient and cost-effective to maintain and operate in the production of biodegradable plastics, Mason Lu from Neway Valve tells OGN
In 2019, at the deepest point of the ocean, the Mariana Trench, 11,000 m below the surface, there was no sign of life, but evidence of human activity was found - plastic.
Plastic is one of the most important basic materials in modern industry. According to Our World in Data, from 1950 to 2015, humans produced 5.8 billion tonnes of plastic waste, of which over 98 per cent was landfilled, abandoned, or incinerated, and less than 2 per cent was recycled.
In recent years, global efforts have been made to achieve the ‘carbon reduction’ goal, and in 2022, the EU also introduced the ‘Commission adopts Communication on a policy framework for biobased, biodegradable and compostable plastics’ to address plastic pollution.
Biodegradable materials are synthetic materials that can degrade into harmless small molecules under natural conditions.
"Currently, commonly used petroleum-based materials often face challenges in natural degradation. And biodegradable materials serve as alternative products in this context," says Mason Lu from Neway Valve (Suzhou).
 |
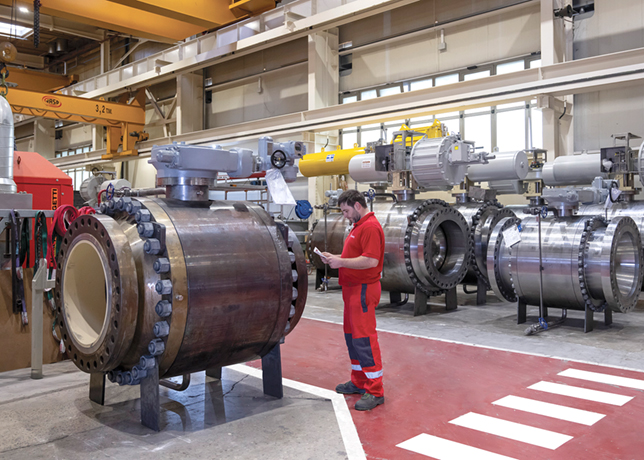
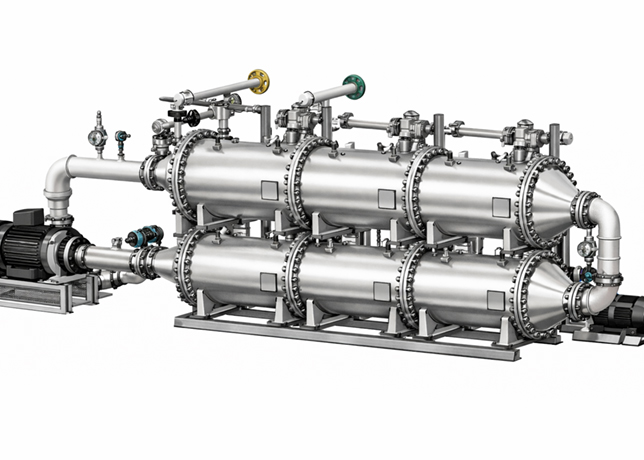
A Neway typical bellows seal globe valve |
Biodegradable materials can be further divided into bio-based biodegradable materials and petroleum-based biodegradable materials.
In recent years, with the continuous maturation of production technology and the phasing out of policy requirements, the global and domestic market sizes have shown significant growth.
However, they still account for less than 1 per cent of the overall synthetic materials market, indicating significant room for improvement.
The development direction and trends of bio-based and petroleum-based biodegradable materials are closely linked to the key raw material, BDO (1,4-butanediol) to product PBAT/PBS/PET.
DEGRADABLE PLASTICS INDUSTRY CHAIN
BDO and PTA, along with the esterification and condensation of adipic acid, are used to produce biodegradable plastics, which can be used in industries such as plastic bags and bubble tea straws.
PTA is derived from the petroleum refining industry, using PX as a raw material, and PX is obtained from crude oil refining.
Our PX and PTA units have accumulated a wealth of valve application experience, including considerations for acetic acid conditions in coatings, carbon graphite valve conditions, and causes of leakage in PX media.
PBAT TYPICAL UNIT PROCESS
In the continuous esterification process system, AA, PTA, and BDO are mixed in a certain proportion to form a slurry, which is then filled into the reactor.
 |
The conduction oil process |
Through esterification, pre-condensation, final condensation, and viscosity increase processes, qualified PBAT materials are produced.
During the reaction, PBAT also produces a byproduct called tetrahydrofuran (THF). In order to reduce the formation of byproducts, the reaction needs to be carried out under vacuum conditions.
Within the entire process, the thermal medium system is one of the critical devices used to control the reaction temperature of the esterification reactor.
The thermal medium used is conduction oil, with a temperature of around 300 deg C and a pressure of approximately 1.4 Mpa.
The heat transfer oil is heated by the thermal medium pump through the heat exchanger to heat the reaction kettle, and then returned to the conduction oil tank through the return conduction oil pipeline.
TYPICAL VALVE APPLICATION - BELLOWS SEAL GLOVE VALVE
The bellows seal globe valve for conduction oil is one of the commonly used valves in the current system, and it is typically available in two structures: Conventional bellows and anti-erosion type. Currently, our products available for both structures.
The two-piece valve stem structure has the advantage of online maintenance without disassembly.
The vulnerable part of the valve is the operation part, and there is a risk of thread trapped in the valve stem after prolonged use.
In this case, the two-piece valve stem perfectly avoids the drawback of thread trapped, which may lead to pipeline shutdown.
The valve stem consists of an upper valve stem, a stem without threads, and a lower valve stem. The threaded part performs the rotational lifting function, while the stem without threads only moves up and down.
The two valve stem sections are connected by a coupling. The lower valve stem remains stationary, and the threaded component of the upper valve stem can be replaced directly, achieving the online maintenance function without disassembly.
In addition, Euro Chlor is the design standard of the European Chlorine Association. In the Euro Chlor design standard, the two-piece valve stem is also mentioned as permissible.
Section 14.4 specifies that it can be either one-piece or two-piece. However, in the BS 1873, API 623, and API 602 design standards, only the one-piece valve stem is allowed.
However, this does not mean that one-piece or two-piece valve stems are inherently better or worse.
Different application scenarios may require different valve stem structures.
The goal is to ensure the safe operation of the valve while making it more convenient, efficient, and cost-effective in terms of maintenance and operation.