 Al-Kaabi ... advocating for a balanced and realistic energy transition
Al-Kaabi ... advocating for a balanced and realistic energy transition
As the world looks to boost energy security and transition to less carbon emitting fuels, the role of natural gas is crucial, and Qatar is stepping up to lead with its vast reserves
Qatarenergy continues to establish itself as one of the world's largest providers of liquefied natural gas (LNG), recognising its role in the energy transition and addressing energy demand.
Its efforts span from bolstering production capacity in Qatar to the development of the Golden Pass LNG export project in the US, in addition to its commitments to various LNG receiving terminals in Europe, including the Montoir-de-Bretagne LNG Terminal in France.
With substantial energy demand growth in the coming decades, global LNG supplies are crucial for meeting this demand.
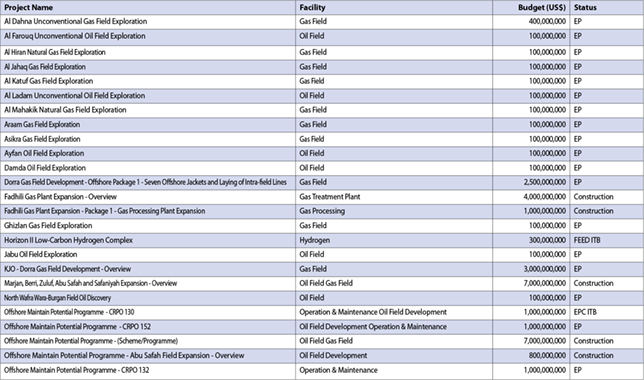
Currently, the company is implementing its North Field East Project (NFE), which will raise LNG production capacity from 77 million tonnes per annum (MPTA) currently to 110 MPTA. NFE represents the first phase of Qatar’s planned LNG expansion.
In early October, Qatar also moved on the second phase of its LNG expansion on project, the North Field South Project (NFS), which will significantly increase its production capacity from the current 77 MTPA to 126 MTPA by 2026.
The importance of the project can be gauged from the fact that His Highness Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani, Amir of the State of Qatar, personally laid the foundation stone.
Saad Al-Kaabi, the Minister of State for Energy Affairs, the President and CEO of QatarEnergy, highlighted the importance of natural gas for a balanced and realistic energy transition.
In remarks at the Tokyo Green Transformation Week, Al-Kaabi expressed firm belief that 'a balanced energy transition demands the incorporation of natural gas in our present and future energy,' and that 'natural gas will be indispensable, especially given its reliability as a base-load source for many nations and for many years post-2050'.
He added: 'While the pivot towards renewables is commendable, they cannot be the sole solution, particularly considering their intermittent nature. That's where natural gas, as a cleaner, cost-effective, and ready-to-use component of energy transition, becomes vital.'
Emphasising a future vision for Qatar’s LNG industry, QatarEnergy in September announced changing Qatargas’ name to QatarEnergy LNG.
With a new name and logo, QatarEnergy LNG will continue to deliver on its commitment to safety, environmental protection, project delivery and the reliability and efficiency of its production facilities.
LONG-TERM LNG SUPPLY AGREEMENTS
 |
The expansion of the North Field will significantly increase Qatar's LNG |
Recently, QatarEnergy signed long-term LNG supply agreements with major European energy companies Eni, Shell, and TotalEnergies for Italy, Netherlands, and France.
In October, 23 affiliates of QatarEnergy and Eni signed a long-term LNG sale and purchase agreement (SPA) for the supply of up to 1 MTPA of LNG from Qatar to Italy.
Accordingly, LNG will be delivered to FSRU Italia, a floating storage and regasification unit, located in the port of Piombino, in Italy’s Tuscany region.
LNG deliveries are expected to start in 2026 for 27 years and will be sourced from the joint venture between QatarEnergy and Eni, where the latter is a partner in the 32 MTPA NFE expansion project with a 3.125 per cent share.
In the same month, QatarEnergy and Shell signed two long-term agreements for the supply of up to 3.5 MTPA of LNG from Qatar to the Netherlands.
According to the agreement, LNG will be delivered to Gate LNG terminal located in the port of Rotterdam starting in 2026 for 27 years.
The LNG volumes will be sourced from the two joint ventures between QatarEnergy and Shell, where the latter holds a 6.25 per cent share in the 32 MTPA NFE project and a 9.375 per cent share in the 16 MTPA NFS project.
Furthermore, in October, QatarEnergy and TotalEnergies signed two long-term LNG agreements for the supply of up to 3.5 million tons per annum (MTPA) of LNG from Qatar to France.
Accordingly, LNG will be delivered to the Fos Cavaou LNG receiving terminal in southern France, with deliveries expected to start in 2026 for a term of 27 years.
The LNG volumes will be sourced from the two joint ventures between QatarEnergy and TotalEnergies.
TotalEnergies’ partnership in the North Field LNG Expansion Projects is made up of a 6.25 per cent share in the NFE project and a 9.375 per cent share in the NFS project.
Besides LNG agreements, QatarEnergy has signed a 10-year naphtha supply agreement with Japan-based Marubeni Corporation, a leading integrated trading and investment business conglomerate.
The agreement, signed by QatarEnergy on behalf of Qatar Petroleum for the Sale of Petroleum Products Company (QPSPP), stipulates a supply of up to 1.2 MPTA of naphtha to Marubeni starting from October 2023.
This agreement builds on a five-year naphtha sales agreement signed in 2018, which expired in September 2023.
QatarEnergy and Marubeni Corporation have a long-standing strategic partnership through several shared investments in the energy industry in Qatar, including investment in Al-Kharsaah solar power plant and Mesaieed power plant.
LOCAL & GLOBAL ENERGY CONTRACTS
QatarEnergy continues to demonstrate its commitment to global energy markets through investments both at home and abroad.
In October, QatarEnergy won a new exploration block offshore Egypt as part of the 2022 EGAS international bid round.
The results of the bid process were announced by Egypt’s Ministry of Petroleum and Mineral Resources, awarding exploration and production rights for block EGY-MED-E8 (East Port Said) to a consortium comprising QatarEnergy (33 per cent), ENI (Operator, 34 per cent ) and BP (33 per cent).
This award solidifies QatarEnergy’s position in Egypt’s upstream sector with a total of four offshore exploration blocks, including interests in Red Sea Blocks 3 and 4, and the North Marakia Block in the Mediterranean Sea.
Before that in March, QatarEnergy announced a light oil discovery in the Jonker-1X deep-water exploration well in the PEL-39 Exploration License, offshore Namibia. The well was drilled to a total depth of 6,168 m in a water depth of 2,210 m.
QatarEnergy is part of a consortium with Shell (the operator) and the National Petroleum Corporation of Namibia (Namcor) in the PEL-39 Exploration License.
Also in March, QatarEnergy entered into a farm-in agreement with ExxonMobil Canada for two exploration licenses offshore the province of Newfoundland and Labrador in Canada.
QatarEnergy holds a 28 per cent working interest in license EL 1167, where the Gale exploration well and associated activities are planned. It also holds a 40 per cent working interest in license EL 1162.
In the following month of April, QatarEnergy entered into an agreement with Shell to acquire a 40 per cent working interest in the C-10 block located offshore Mauritania; while in Iraq, QatarEnergy got a 25 per cent share in the Gas Growth Integrated Project (GGIP) - a multi-billion-dollar project aimed at monetising and developing Iraq’s natural gas resources.
Later in June, QatarEnergy, and its joint-venture partners TotalEnergies, Petrobras, and Petronas Petróleo Brasil (PPBL) signed the production sharing contract (PSC) for the Agua-Marinha block in Brazil.
The block has a total area of 1,300 sq km and is located in water depths of about 2,000 m within the prolific Campos Basin.
At home, QatarEnergy and Chevron Phillips Chemical Company (CPChem) announced they had secured $4.4 billion financing for the Ras Laffan Petrochemicals project, a world scale integrated polymers complex in Ras Laffan Industrial City, Qatar.
The Ras Laffan Petrochemicals project is a joint venture between QatarEnergy (70 per cent) and CPChem (30 per cent) and is considered the largest petrochemical project in Qatar for which Final Investment Decision was announced in January 2023.
The complex, expected to begin production in late 2026, consists of an ethane cracker with a capacity of about 2.1 million tons of ethylene per annum.
It also includes two polyethylene trains with a combined output of 1.7 million tons per annum of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) polymer products, which are used in a wide range of applications, including packaging, construction, and consumer goods.
This complex will raise Qatar’s overall petrochemical production capacity to almost 14 million tons per annum, and it is expected to generate significant economic benefits for the country, including increased tax revenue and foreign investment.
Separately, QatarEnergy signed an agreement with Korea’s HD Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) for the construction of 17 ultra-modern LNG carriers.
The deal, valued at QR14.2 billion ($3,9 billion), marks the start of the second phase of QatarEnergy's LNG ship acquisition programme, which will support its expanding LNG production capacity from the North Field LNG expansion and Golden Pass LNG export projects as well as its long-term fleet replacement requirements.
Together with the 60 ships that were contracted by QatarEnergy in the first phase of the programme–and to be built at Korean and Chinese shipyards–the latest agreement brings the total number of confirmed new LNG vessels to be delivered to QatarEnergy and its affiliates to 77.
CONCLUSION
Qatar’s commitment to ensure continued and reliable supplies of energy to Europe and the rest of the world is underpinned by its substantial and ongoing investments across the entire gas value chain.
In the words of Al-Kaabi: 'Our efforts span from bolstering production capacity in Qatar to the development of the Golden Pass LNG export project in the US, in addition to our commitments in various LNG receiving terminals in Europe, including the Montoir-de-Bretagne LNG Terminal in France.'
He said: 'We are proud that our new LNG expansion in Qatar is the least carbon intensive project in the world.'
By ZAINAB AL TAITOON