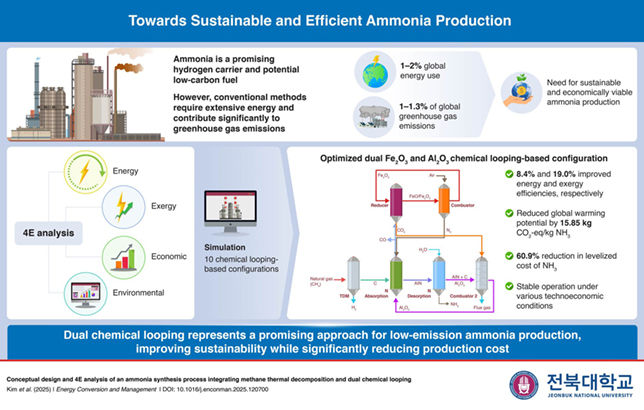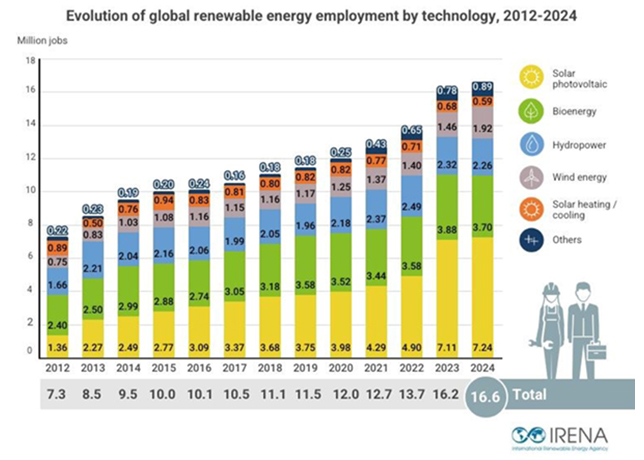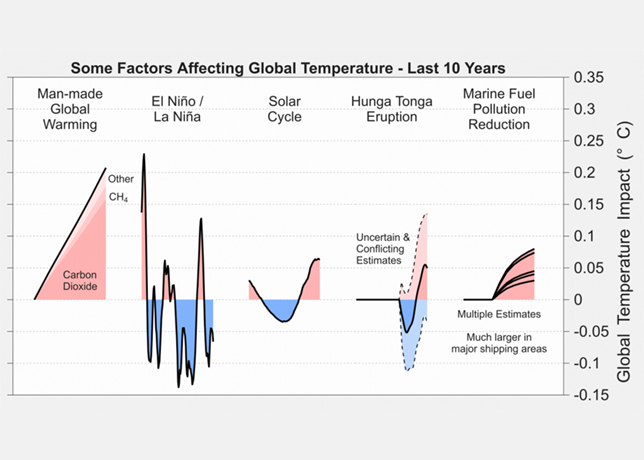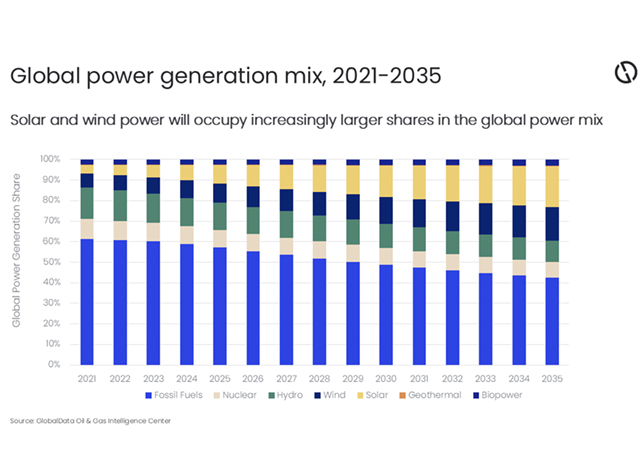
MH Hydraulics, a leading hydraulic solutions provider in the Middle East, discusses the various points to remember while choosing pipes and clamps for hydraulic systems
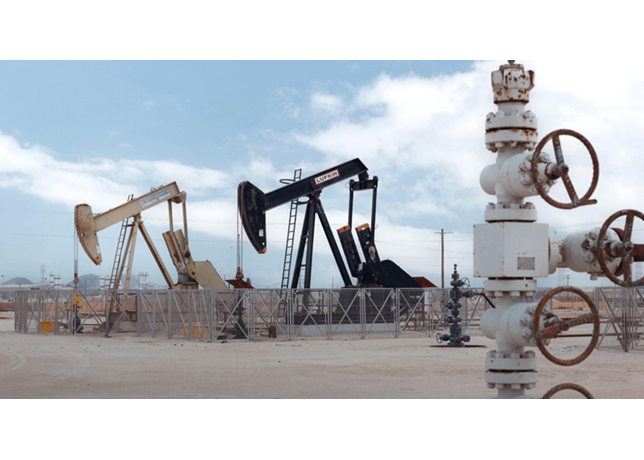
Choosing the right pipes and clamps is of high importance in the design and installation of any hydraulic system as it has a major impact on the efficiency and life expectancy of the system while contributing to energy saving and safety.
Seamless carbon steel or stainless steel pipes are always used for hydraulic rigid piping because of their high strength, low price, and easy leak-free connection. They should not be galvanised because zinc flakes and can mess up O-rings and seals.
Cold drawn low carbon pipes are preferred because they can be easily welded to various standard pipe fittings. But where corrosion resistance is required, stainless-steel seamless pipes should be used.
Hydraulic tubes should be chosen based on the system hydraulic pressure, flow rate, and application. The inner and outer wall of pipes should not be rusted, uneven, or elliptical. They must be smooth, without oxidation, and free from defects.
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) is used to size the hydraulic pipes, with NPS referring to the inside diameter for those up to 12', and outside diameter for pipes above that size. Schedule numbers for hydraulic pipes are given depending on their wall thickness, with #10 being a light wall and #160 being extra-extra strong. The most common pipe schedule used is #40 because it has the minimum wall thickness good for hydraulic systems and is easily available in the market.
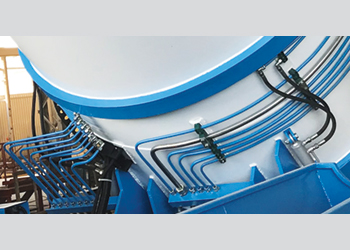
Selection of right pipe clamps as well as ensuring correct spacing of them are equally important to design a safe and reliable hydraulic system. Factors to be considered are the hydraulic line pressure, weight to be supported and the dynamic load, apart from the size and application.
Complete clamps will consist of weld plates, body, cover plate, and a set of screws. The weld plates, cover plates and screws are available in mild carbon steel for normal application, 304 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel for corrosive environments.
The clamp body is generally made up of polypropylene, polyamide, or aluminium depending on the temperature range of the applications. Choosing cheap clamps that that don’t have specified material certification is prone to risks.
There is a diverse choice of clamps available depending on the application. The technical article in our online edition (https://ognnews.com/) elaborates on the various clamps and their uses.
To conclude, a well-chosen hydraulic pipe and clamp system will enable smooth transfer of hydraulic energy and can keep vibration and noise levels to minimum level. MH Hydraulics can provide technical advice on any hydraulic piping and clamping system and, with its certified repair centres (CRCs), it can install, flush, and commission complete hydraulic systems.