INDUSTRY ESTIMATES that the Current IT technology provides ten folds the processing power that was available 5 years ago and would have cost twice as much.
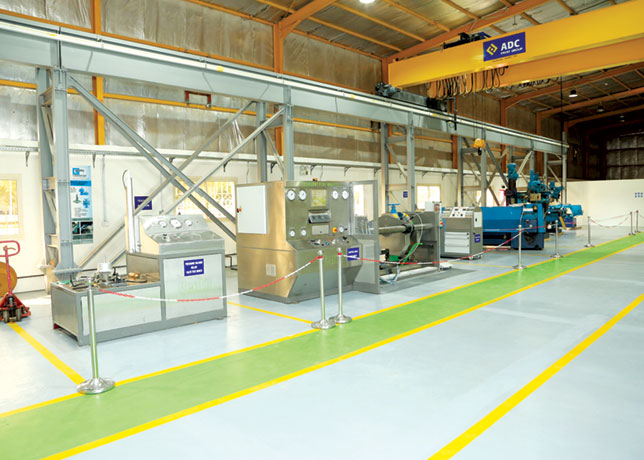
One of the largest such applications anywhere, the new blade server technology is a quantum leap forward in computing capacity where accuracy of massive amounts of geophysical data and reservoir simulation is an absolute requirement.
Consolidating servers into centralised data centers also allows Saudi Aramco to increase its computing power and reduce its space utilisation. Server consolidation reduces the challenges and costs associated with administering many small servers scattered across an enterprise.
Physical consolidation has generally involved replacing bulky tower servers with slender 1U or 2U rack systems as they take less space and place the servers and infrastructure within easy reach of the administrator. These servers enable organizations to benefits from consolidation, yet because each server requires its own infrastructure - including cables for power, Ethernet, systems management, power distribution units (PDUs), keyboard/video/mouse (KVM) switches and Fibre Channel switches - each offer challenges of their own. A rack of 42 1U servers can have hundreds of cables strung throughout the rack, making it difficult to determine which cables attach where and complicating the addition and removal of servers from the rack. In addition, the PDUs and switches consume valuable rack sidewall space.
A blade server is a type of rack-optimized server that eliminates many of these complications, providing an effective alternative to 1U and 2U servers. There is a range of blade server designs - from ultradense, low-voltage, lesser-performing servers to high-performance, lower-density servers to proprietary, customized rack solutions - that include some blade features.
“Blade server” refers to a chassis that can hold a number of hot-swappable devices called blades. Blades come in two varieties: server blades and option blades. A server blade is an independent server, containing one or more processors and associated memory, disk storage and network controllers and running its own operating system and applications. Each server blade within a system chassis slides into a blade bay and plugs into a midplane or backplane to share common infrastructure components, such as power supplies, fans, CD-ROM and floppy drives, Ethernet and Fibre Channel switches and system ports.
This blade server architecture is the most efficient solution for adding scale and capacity in a data center. Some blade designs support at least twice as many processors as in a rack-optimised 1U design. The advantages of the blade architecture can include floor/rack space savings, reduced power usage and lower heat output, as well as a potentially lower acquisition cost versus individual rack-optimized servers. Blade servers can also help reduce administration costs and improve systems management by consolidating dozens of widely distributed servers into one rack. Most blade server chassis can be added to a standard rack along with traditional rack servers.
Blade server benefits
Blade servers offer modular scalability, versatility, performance, availability, system management and deployment, as well as cost saving - in one package. The modular blade server architecture offers the flexibility needed to accomplish each of these requirements. The following topics explore the benefits of blade servers in these areas:
A larger chassis that allows for greater expansion through option modules helps to balance performance vs. density to properly leverage the infrastructure for optimum utilization. Without this flexibility, the blade server might have great density with poor performance or great performance with low density and not achieve the desired benefits.
Versatility. Conventional server designs are limited to only one type of processor per server. Blade architecture imposes no such limitations. Advanced chassis designs with sophisticated cooling and power technologies can support a mix of blades containing different types and speeds of processors today, and hotter, faster processors in the future. This provides investment protection as technology evolves. Each blade is a self-contained server, running its own operating system and software.