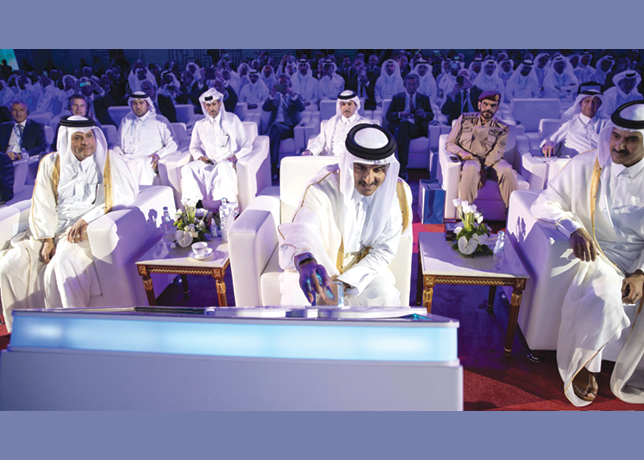
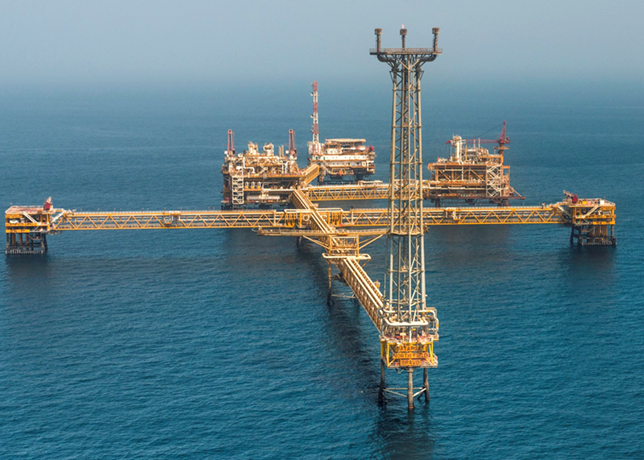
The Amir of Qatar Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani laying the foundation stone of the North Field expansion project
The Amir of Qatar Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani laying the foundation stone of the North Field expansion project
The country’s energy sector has embarked on transformational journey, expanding LNG capacity whilst diversifying into solar power to meet rising demand and global sustainability targets through strategic investments
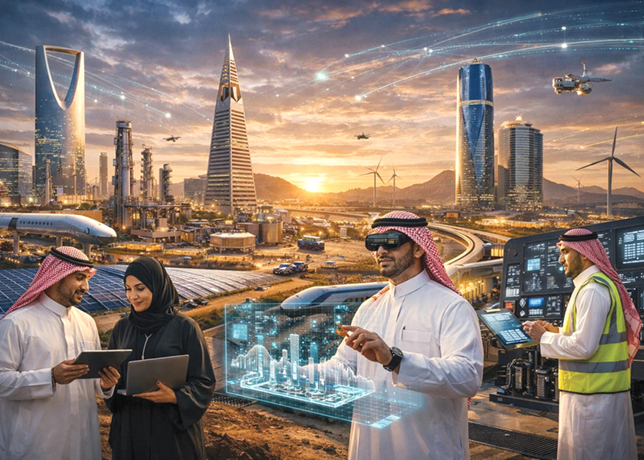
Qatar stands at a pivotal juncture in its energy evolution, masterfully orchestrating a dual strategy that amplifies its traditional hydrocarbon dominance whilst embracing renewable energy technologies.
The year also saw Qatar announcing huge investments in petrochemicals, fertiliser and renewable projects that collectively position the nation as a formidable energy powerhouse capable of meeting both current global demands and future sustainability imperatives.
The Gulf state’s ambitious expansion plans reflect a sophisticated understanding of global energy dynamics, where traditional fossil fuels continue to play essential roles alongside emerging clean technologies.
As international energy markets grapple with supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions, Qatar has emerged as a stabilising force, leveraging its geographical advantages and vast reserves to secure long-term partnerships whilst simultaneously investing in next-generation energy infrastructure.
LEGACY ENERGY & FUTURE VISION
Qatar’s energy strategy has undergone substantial evolution from its historical reliance on oil exports to becoming the world’s largest LNG exporter.
The small but influential Gulf emirate is rapidly expanding its annual LNG production capacity from the current 77 million metric tonnes (MT) to 142 MT by 2030, an 85 per cent increase, positioning itself to control nearly 25 per cent of global LNG trade.
This transformation reflects the nation’s prescient understanding that natural gas would serve as a crucial transitional fuel in the global energy transition.
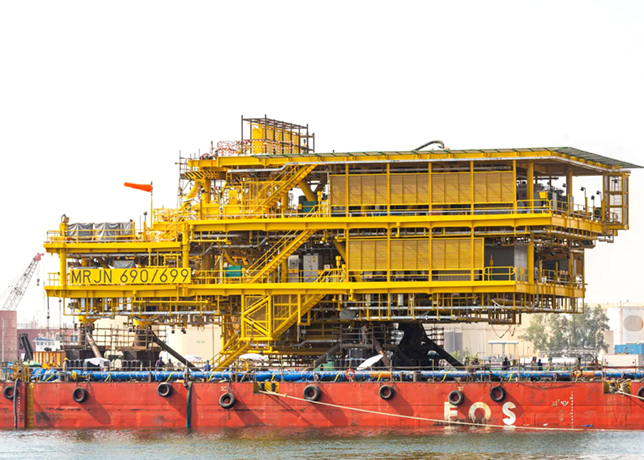
This massive expansion encompasses the North Field project, which represents the largest natural gas development in the industry’s history.
The Qatari leadership has increasingly sought to diversify the country’s economy, venturing into sports, telecommunications, and logistics, even as it continues to increase exports of energy commodities.
The coutnry’s National Vision 2030 emphasises sustainable development whilst maintaining economic prosperity through diversified energy portfolios.
The vision extends beyond mere production increases, encompassing comprehensive value chain integration and technological advancement.
This strategic approach acknowledges global climate commitments whilst recognising natural gas’s role as a bridge fuel, particularly in emerging markets where coal displacement remains a priority.
The vision covers both supply security for international partners and domestic energy sustainability through renewable integration.
CURRENT DEVELOPMENTS & MARKET DYNAMICS
 |
Qatar is the world’s largest LNG exporter, producing 211 billion cu m annually |
Qatar’s energy sector witnessed remarkable momentum throughout 2025, with multiple flagship projects that will boost the country’s production capabilities in LNG, oil, petrochemical and renewable energy portfolios.
The North Field expansion project continues progressing through its various phases, with construction activities accelerating across multiple development areas.
International partnerships have strengthened considerably, with major oil companies including ExxonMobil, Shell, and TotalEnergies securing substantial stakes in different project phases.
Recent market developments indicate robust demand for Qatari energy products, particularly from Asian markets where economic growth drives energy consumption.
The petrochemicals sector has experienced unprecedented growth, and Saad Al Kaabi, Qatar’s Minister of Energy and CEO of state-owned QatarEnergy, has highlighted significant production increases.
'We have increased our petrochemical production by almost 130 per cent. We are building the largest polythene plant in the Mena region here in Qatar.'
This diversification represents strategic value addition to hydrocarbon resources.
Current discussions within the sector focus on supply chain optimisation, technological innovation, and sustainability integration.
Industry insiders report increasing emphasis on carbon capture technologies and methane emission reduction across all operations.
STRATEGIC STRENGTHS & COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
Qatar’s energy sector derives its strength from multiple converging factors that create unprecedented competitive advantages.
The North Field, containing approximately 15 per cent of global proven natural gas reserves, provides the foundation for sustained production growth over multiple decades.
Geographical positioning offers strategic advantages for both production and distribution. Qatar’s location provides efficient access to major consumption centres across Asia, Europe, and emerging markets.
The nation’s investment in world-class infrastructure, including expanded LNG terminals and advanced shipping capabilities, reinforces these natural advantages.
Technological leadership represents another crucial strength, with Qatar consistently adopting cutting-edge extraction, processing, and transport technologies.
The integration of artificial intelligence, advanced materials, and automation across operations enhances efficiency whilst reducing environmental impact.
Financial stability enables sustained investment in both traditional and renewable projects. Qatar’s sovereign wealth fund and robust fiscal position provide the resources necessary for long-term strategic initiatives, including the massive capital requirements associated with LNG expansion and renewable development.
The nation’s commitment to human capital development through comprehensive Qatarisation programmes ensures domestic expertise growth.
'We have never wavered in our commitment to giving opportunities to young Qataris to build rewarding careers and to develop our national competencies in almost every field,' stated Minister Al-Kaabi.
OPTIMAL STRATEGIC PATHWAY FORWARD
Qatar’s optimal energy future lies in the sophisticated integration of legacy hydrocarbon resources with strategic renewable development, rather than exclusive focus on either approach.
This dual-track strategy maximises existing advantages whilst building capabilities for long-term sustainability.
Natural gas will continue serving as Qatar’s primary revenue generator and global market differentiator for the foreseeable future.
The substantial investments in LNG infrastructure and long-term contracts provide revenue stability that enables renewable energy investments without compromising economic growth.
The renewable energy strategy should focus on domestic consumption displacement and export potential development.
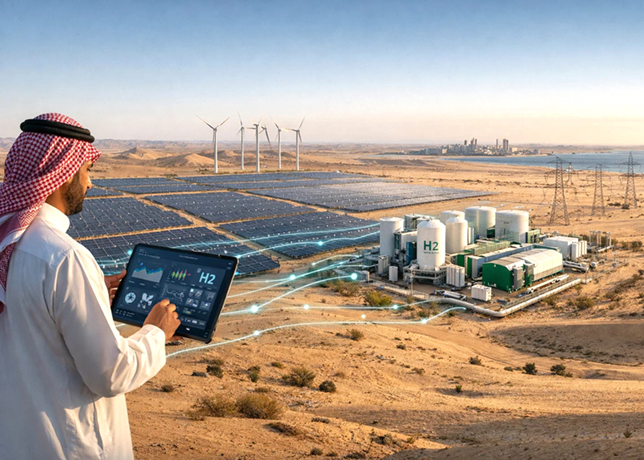
In 2022 Qatar’s first solar power project came online, supplying the country with 7.5 per cent of its electricity needs, with two more solar projects scheduled for completion in 2025, establishing a foundation for expanded renewable capacity.
Strategic partnerships with international technology leaders can accelerate renewable deployment whilst leveraging Qatar’s financial resources and project management expertise.
The nation’s experience managing large-scale energy projects provides transferable skills applicable to renewable development.
Carbon management technologies represent crucial complementary investments, enabling continued hydrocarbon production whilst addressing climate concerns.
Qatar’s investment in carbon capture, storage, and utilisation technologies demonstrates commitment to responsible resource development.
Regional leadership in clean technology deployment could position Qatar as a renewable energy hub for the broader Middle East, leveraging existing infrastructure and expertise to support regional decarbonisation efforts.
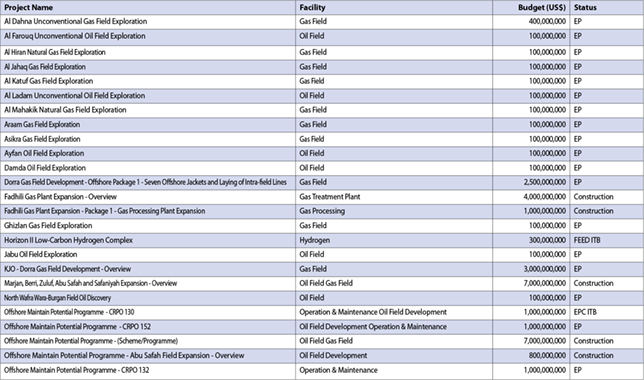
MAJOR ENERGY PROJECTS & INITIATIVES
Current project portfolios encompass both traditional and renewable energy developments across multiple scales and timeframes. These include 572 large projects, 1,433 small and medium-sized projects, and 671 industrial initiatives.
The North Field East and North Field South expansions represent the largest components of Qatar’s energy infrastructure development.
These projects involve multiple international partners and will add approximately 49 million tonnes of annual LNG production capacity through dedicated trains and processing facilities.
Samsung C&T will handle the engineering, procurement and construction of the solar power plants, which were scheduled to be commissioned by the end of 2029.
The 2-GW solar development programme represents Qatar’s most ambitious renewable energy initiative, encompassing multiple installation sites across the country.
The Al Kharsaah solar power plant serves as Qatar’s renewable energy flagship. The Al Kharsaah solar power plant was built in two phases of 400 megawatts-peak (MWp) each, and, therefore, has a full capacity of 800 MWp.
This facility demonstrates Qatar’s commitment to large-scale renewable deployment whilst providing valuable operational experience.
Petrochemical expansion projects include major polythene and fertiliser facilities that leverage Qatar’s abundant feedstock resources.
These value-added developments enhance revenue diversification whilst creating downstream integration opportunities.
Private sector participation continues expanding through various partnership structures and investment frameworks. International companies increasingly view Qatar as an attractive destination for energy infrastructure investments due to regulatory stability and market access advantages.
GEOGRAPHICAL & STRATEGIC POSITIONING ADVANTAGES
Qatar’s geographical position provides exceptional advantages for energy leadership across production and distribution dimensions.
The nation’s location enables efficient resource access to major consumption centres whilst offering strategic depth for supply chain resilience.
Maritime access through the Arabian Gulf facilitates efficient LNG transport to Asian markets, which represent the fastest-growing segment of global gas consumption.
Qatar’s shipping infrastructure and port facilities rank among the world’s most advanced, enabling cost-effective global distribution.
The nation’s stable political environment and robust regulatory frameworks provide the predictability essential for long-term energy investments.
International partners consistently cite regulatory clarity and investment protection as key factors in their Qatar engagement decisions.
Regional positioning offers opportunities for energy interconnection and cooperation. Qatar’s potential role as a regional renewable energy hub could leverage existing infrastructure whilst supporting broader Middle Eastern decarbonisation efforts.
Climate conditions, whilst challenging for some applications, provide exceptional solar radiation resources that enable highly efficient photovoltaic generation.
The combination of abundant solar resources and available land creates significant potential for large-scale renewable development.
Qatar’s strategic relationships with major energy consuming nations provide market access advantages that smaller producers cannot achieve.
Long-term partnerships with Asian governments and major corporations ensure sustained demand for Qatari energy products.
DOMESTIC NEEDS & CONSUMPTION PATTERNS
Qatar’s domestic energy consumption continues growing driven by economic diversification, population expansion, and industrial development.
Currently, thermal generation accounts for more than 90 per cent of Qatar’s total electricity generation capacity, standing at 12 GW.
Air conditioning represents the largest component of domestic electricity consumption due to climatic conditions, creating substantial peak demand during summer months.
This consumption pattern aligns well with solar generation profiles, providing opportunities for renewable integration.
Industrial energy requirements continue expanding as Qatar develops downstream processing capabilities in petrochemicals, fertilisers, and manufacturing.
These industrial consumers often require reliable baseload power that natural gas generation can provide efficiently.
Water desalination represents another significant energy consumer, with Qatar’s limited freshwater resources necessitating energy-intensive treatment processes.
The integration of renewable energy with desalination facilities offers potential efficiency improvements and cost reductions.
Qatar’s renewable sector includes the Siraj 1 solar power plant in Al Kharsaah, with a capacity of 800 MW, and over 9 MW from other distributed solar energy projects.
Current renewable capacity provides approximately 7.5 per cent of electricity needs, with targets reaching 18-20 per cent by 2030.
Future consumption growth will likely accelerate as Qatar’s economic diversification efforts mature and new industrial facilities commence operations.
The nation’s commitment to hosting major international events and developing tourism infrastructure will further increase energy demands across multiple sectors.
FUTURE OUTLOOK
Qatar’s energy sector stands positioned for continued global leadership through strategic expansion of both traditional and renewable capabilities.
The nation’s approach of leveraging existing strengths whilst building future capabilities provides a sustainable pathway for long-term prosperity.
Continued investment in LNG infrastructure and technology will maintain Qatar’s competitive advantages in global gas markets, particularly as demand growth accelerates in emerging economies seeking to displace coal consumption.
The North Field expansion projects ensure sustained production capacity through multiple decades.
Renewable energy development should focus on achieving domestic consumption targets whilst exploring export opportunities through interconnection projects and clean energy partnerships.
The 20 per cent renewable target by 2030 provides a realistic foundation for subsequent expansion phases.
Research and development investments in clean technology, carbon management, and energy efficiency will position Qatar as a technology leader whilst supporting responsible resource development.
Partnerships with leading universities and research institutions can accelerate innovation adoption.
Regional energy cooperation offers opportunities for market expansion and technology deployment.
Qatar’s role as a regional clean energy hub could leverage existing infrastructure and expertise whilst supporting broader decarbonisation efforts across the Middle East.
The integration of digital technologies and artificial intelligence across energy operations will enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve environmental performance.
Qatar’s commitment to technological advancement provides competitive advantages in increasingly sophisticated energy markets.
By Abdulaziz Khattak