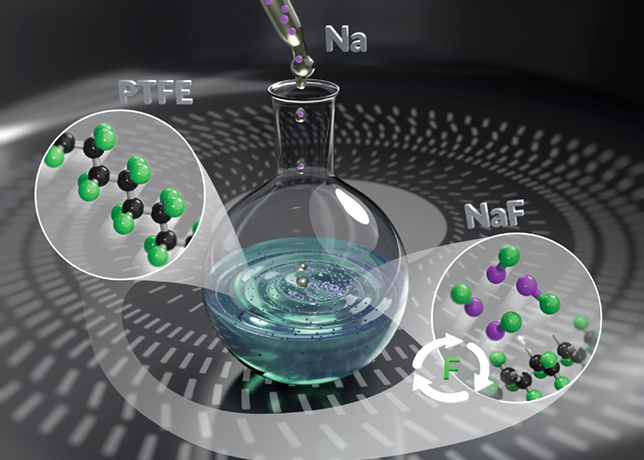
Researchers at Nagoya Institute of Technology have developed an innovative method for recycling polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) under mild conditions.
Their study, published in Nature Communications, achieved up to 98 per cent fluorine recovery at room temperature using sodium dispersion, addressing the limitations of traditional energy-intensive defluorination methods.
This eco-friendly technique also effectively transforms various PFAS compounds, highlighting its broad applicability.
The researchers emphasise that this method minimises environmental hazards and enhances fluorine recovery, potentially reducing reliance on conventional fluorine sources.