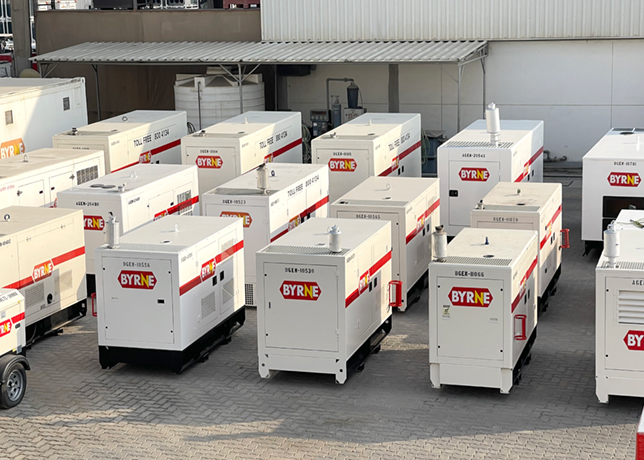
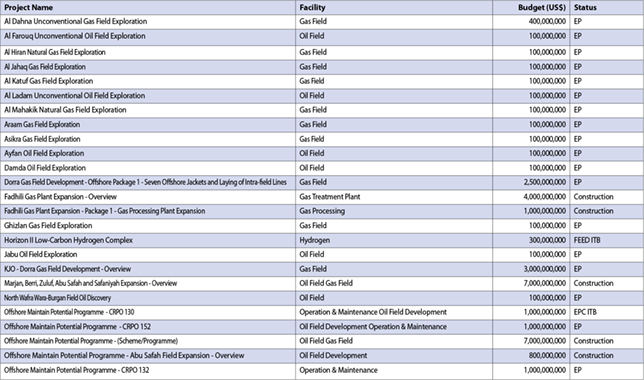
The new system at EXPEC uses IBMÕs advanced clustering technology of x330 eServers
The new system at EXPEC uses IBMÕs advanced clustering technology of x330 eServers
Saudi Aramco has implemented the largest supercomputer in the region, and one of the largest such systems in the world.
Built extremely cost-effectively, the new supercomputer at Saudi Aramco's EXPEC Computer Centre is based on the open source Linux operating system running on IBM Intel-based servers, using clustering technology from IBM. It will be used for advanced modelling and analysis in petroleum exploration and oilfield development.
The new system is a groundbreaking application of new Linux clustering technologies, which allows organisations to take off-the-shelf Intel-based servers and link them together to build massively parallel supercomputing systems.
The new system at Saudi Aramco's EXPEC Computer Centre (ECC) clusters 896 IBM x330 eServers, and uses IBM's advanced clustering technology. The system was implemented with the help of technical experts from Saudi Business Machines (SBM), IBM's general marketing and services representative in Saudi Arabia.
Super-fast computer systems have become vital to the oil and gas industry as they allow oil producers to discover viable new fields faster. Accurate computer models and simulations made of reservoirs and wells optimise the extraction of hydrocarbons from known reserves. This sophisticated new technology allows geoscientists to gather more detailed data about the subsurface, and analyse it more intelligently to help them make better decisions and conduct long-term planning regarding exploration and development.
This allows a better return on the massive investment companies such as Saudi Aramco make in conducting drilling operations. Accurate reservoir modelling also means that the scientists have a more accurate view of Earth layers and the position of the oil and gas content, meaning that the life of the reserves can be extended.
EXPEC is a pioneer in the use of Unix and Linux clusters for oil and gas applications, having implemented a 512-node cluster based on IBM SP UNIX clustering technology early last year, and implemented a 64-node (128-processor) Linux cluster in October of that year.
This new system consists of seven sub-clusters, each with 128 nodes of IBM x330 servers, with two processors per node, giving the total of 1,792 processors. The cluster has 35 terrabytes (1TB is approximately 1,000,000MB) of IBM SCSI-attached storage.
A unique feature of EXPEC's installation is that the various clusters that it has implemented are all brought together in one huge network of sub-clusters. This brings simplicity and flexibility in managing the systems and distributing workload.
The Linux operating system used in this supercomputing cluster is ideal for EXPEC's application, as it is best suited to tasks that require massive amounts of processing power, but do not have a requirement for supporting many client systems, or sharing information with other applications or databases (such as in Web or e-commerce systems). The EXPEC system uses special (patented) algorithms that Aramco designed to efficiently process the seismic data, with third party applications for seismic processing and high-end visualisation systems.
This system was delivered and implemented for Saudi Aramco in only two weeks, a record time for such a complex task, by the team from IBM and SBM.
IBM is the world leader in producing supercomputing solutions, creating five of the top 10 supercomputing systems in the world. IBM leads the industry with a 33 per cent share of installed performance (source Top500.org, using the LINPACK Benchmark).
IBM is the world's largest information technology company, with more than 80 years of leadership in helping businesses innovate. IBM creates, develops and manufactures the industry's most advanced information technologies, including customer systems, software, networking systems, storage devices and microelectronics.