The oil and gas industry is shifting towards sustainable solutions while maintaining production in increasingly demanding environments
The oil and gas industry is shifting towards sustainable solutions while maintaining production in increasingly demanding environments
Advanced membrane systems and compact subsea equipment reshape offshore operations whilst gravitational methods maintain dominance onshore
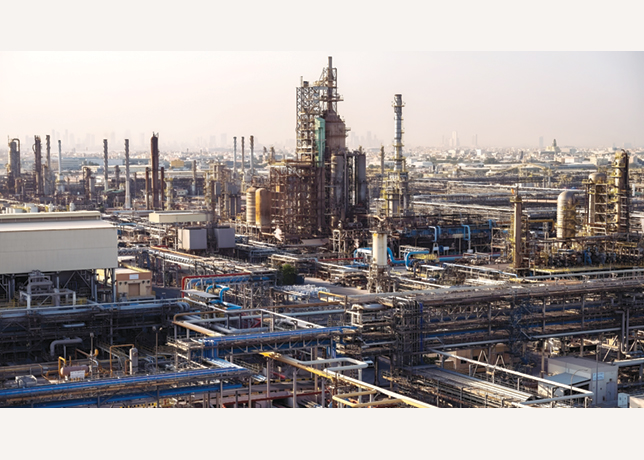
The evolution of separation technology has become inseparable from the oil and gas industry’s capacity to extract hydrocarbons from increasingly challenging environments whilst meeting stringent environmental mandates.
The oil and gas separation market stands at a critical juncture, valued at $14.7 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $19.8 billion by 2033, representing a compound annual growth rate of 3.4 per cent.
This trajectory reflects an industry fundamentally transformed from primitive shotgun separators achieving one to three per cent efficiency in the early 1900s to sophisticated subsea processing systems operating at water depths exceeding 3,000 m.
FROM BASIC TO INDUSTRIAL-SCALE PROCESSING
The genesis of modern separation technology emerged from necessity during the industry’s formative decades.
Early techniques relied exclusively on residence time, employing hay pack separators and rudimentary gravity-based systems that demonstrated woefully inadequate performance metrics.
Companies, such as Facet and Nowata, pioneered the transition towards engineered solutions, introducing cellulose media and steel gauze configurations between the 1920s and 1950s. These innovations enabled more compact equipment designs whilst improving oil-water separation efficiency.
The watershed moment arrived during the 1970s when the establishment of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) catalysed fundamental shifts in separation methodology.
Regulatory pressure forced collaborative ventures between governmental bodies and private enterprises, accelerating the development of cleaner, more efficient technologies.
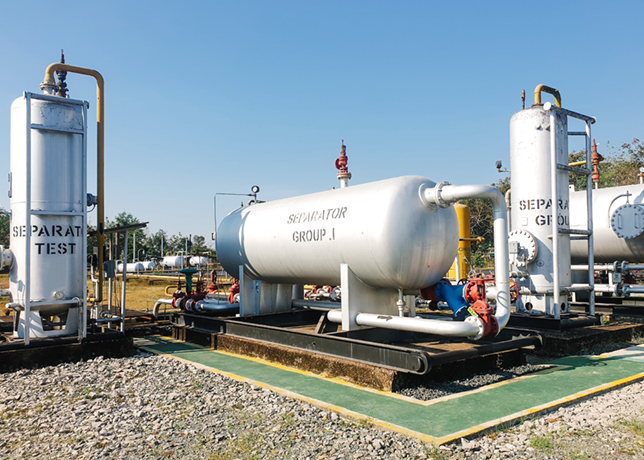
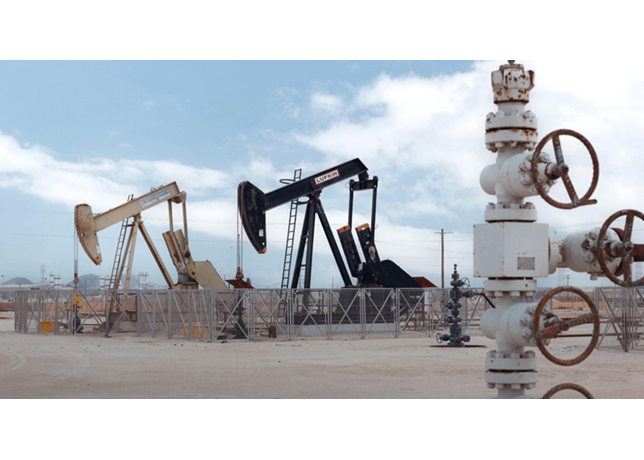
Gravitational separation maintains its position as the dominant technology, accounting for approximately 60.4 per cent of the market in 2024, reported by IMARC Group.
By leveraging natural density differentials between fluids, gravitational separators operate without complex mechanical components, offering low maintenance requirements and robust performance in upstream operations.
Three-phase separators, capable of simultaneously segregating oil, gas, and water in a single unit, commanded 41.3 per cent market share in 2023, demonstrating their critical role in both onshore and offshore installations.
MEMBRANE TECHNOLOGY & HYDROGEN ECONOMY
The emergence of membrane separation technology represents perhaps the most significant advancement in recent decades. The gas separation membrane market, valued at $1.85 billion in 2024, demonstrates explosive growth projected at 6.95 per cent annual growth rate through 2034.
Membrane systems excel in applications ranging from natural gas processing to hydrogen purification and carbon capture, offering energy efficiency advantages over traditional absorption methods.
Air Liquide stands amongst leading innovators, with patent filings demonstrating advanced membrane portfolios including MEDAL membranes, PoroGen membranes, and innovative membrane systems.
In May 2024, Air Products introduced its PRISM GreenSep liquefied natural gas membrane, and received a $113-million European Innovation Fund grant for its ENHANCE project in Antwerp-Bruges, Belgium, establishing Europe’s first industrial-scale renewable ammonia cracking plant.
Polyimide and polyaramide materials dominate the membrane segment with approximately 36 per cent market share in 2024.
These membranes demonstrate particular efficacy in CO2 collection, removing hydrogen sulphide and water in a single step whilst offering lower capex compared to conventional approaches.
Carbon dioxide removal applications constitute the fastest-growing segment, driven by carbon capture, utilisation, and storage initiatives, with the US and Canada collectively accounting for 65 per cent of annual capture capacity.
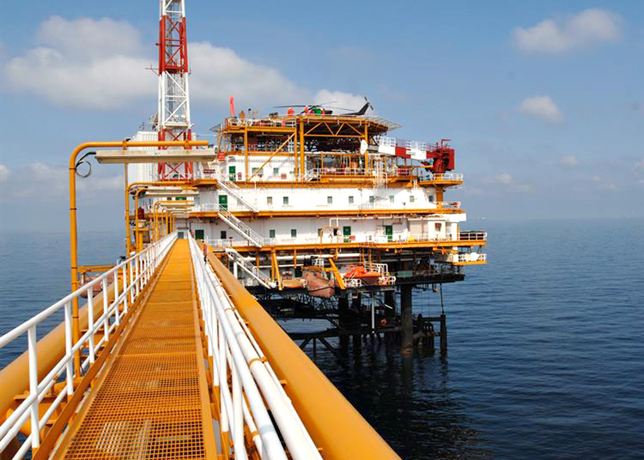
SUBSEA PROCESSING REVOLUTION
The migration towards deepwater and ultra-deepwater developments has necessitated revolutionary advances in compact separation systems.
Conventional cylindrical separator vessels prove infeasible beyond 1,500 m water depth due to wall thickness requirements that limit vessel diameters.
ExxonMobil’s subsea compact separation system, designed for 3,000-m water depths and internal pressures up to 690 bar, exemplifies this technological evolution. Each separation train processes 60,000 barrels per day whilst handling oil gravities ranging from 19 to 38 degrees API, water cuts from zero to 90 per cent, and varying gas-oil ratios.
In August 2024, TotalEnergies’ Libra Consortium approved development of an innovative subsea facility in Brazil’s Mero field, employing HISEP technology to separate and reinject carbon dioxide-rich gas, simultaneously enhancing production and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
These compact systems utilise combinations of centrifugal and gravitational forces, incorporating technologies such as gas-liquid cylindrical cyclones and inline bulk water separators.
Compact electrostatic separators provide efficient methods for heavy oil processing, whilst all-electric control systems enable data-driven performance management.
The modular design approach facilitates installation and retrieval operations, critical considerations given the challenging subsea environment.
North America commands 37.1 per cent of the global separation market, driven by extensive shale gas and tight oil extraction. The region maintains over 1,000 active rigs and exceeds 850,000 producing wells, concentrated in formations including the Permian Basin and Eagle Ford Shale. US government initiatives promoting energy independence and exploration of Alaskan and Gulf of Mexico reserves expand offshore projects, increasing demand for compact and modular separation equipment.
DIGITAL INTEGRATION & FUTURE TRAJECTORIES
Contemporary separation systems increasingly incorporate digital technologies including Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and AI algorithms.
These integrations enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing operational downtime whilst optimising efficiency.
FMC Technologies introduced a compact three-phase separator in early 2024 designed for offshore applications, offering reduced footprint and enhanced operational efficiency, whilst Honeywell developed an AI-integrated separation system in 2023 enabling predictive maintenance.
The shift towards sustainable solutions, optimised energy consumption, and integration of smart technologies positions separation technology as an enabling capability for the industry’s transition towards lower-carbon operations whilst maintaining production economics in increasingly demanding environments.