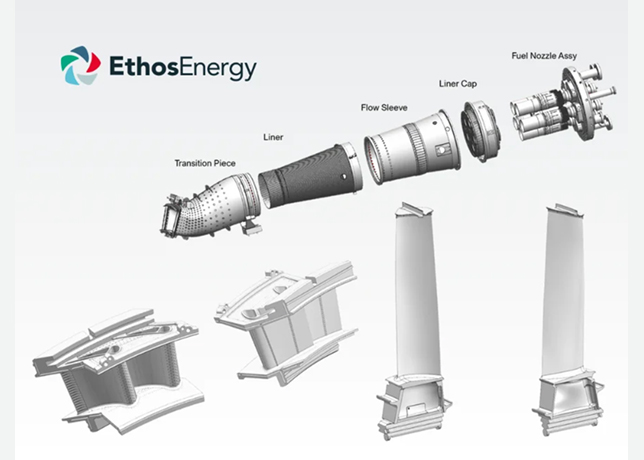
 Temperature-resistant non-metallic liners mitigate corrosion and thermal degradation
Temperature-resistant non-metallic liners mitigate corrosion and thermal degradation
The oil and gas industry in the GCC is evolving with the increasing use of non-metallic materials in piping networks.
The use of non-metallic materials in the GCC's oil and gas sector has seen significant growth.
According to a report by Research and Markets, the demand for non-metallic pipes in the oil and gas sector is expected to grow annually 7.2 per cent from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by the need for more durable and cost-effective piping solutions.
In the GCC, this trend is driven by advancements in materials technology, particularly the introduction of PE raised temperature (PE-RT) and ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE). These materials can withstand higher temperatures (up to 85 deg C) than conventional PE pipes.
"Traditional PE pipes have been favoured for their corrosion resistance and flexibility, but their thermal stability has limited their use in higher temperature applications," says Bhaveth Chali, Technical Manager, Muna Noor Manufacturing and Trading.
PE-RT, a modified version of PE, provides improved thermal stability while maintaining the flexibility and chemical resistance of traditional PE.
ETFE, a fluoropolymer, offers exceptional high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for demanding environments in the GCC's oil and gas operations.
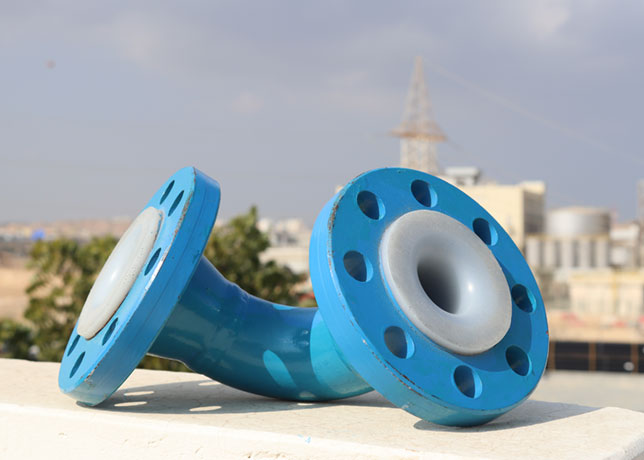
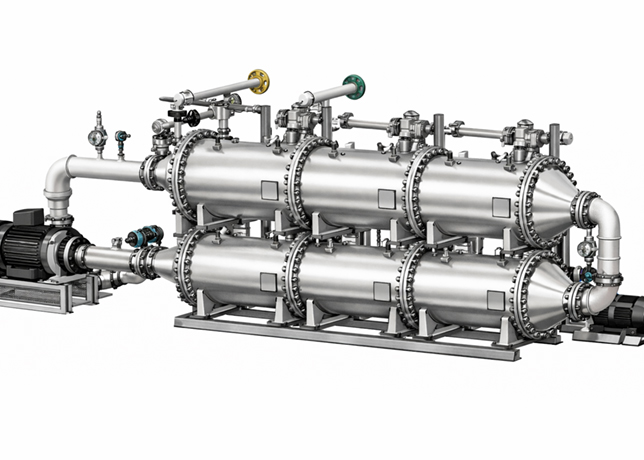
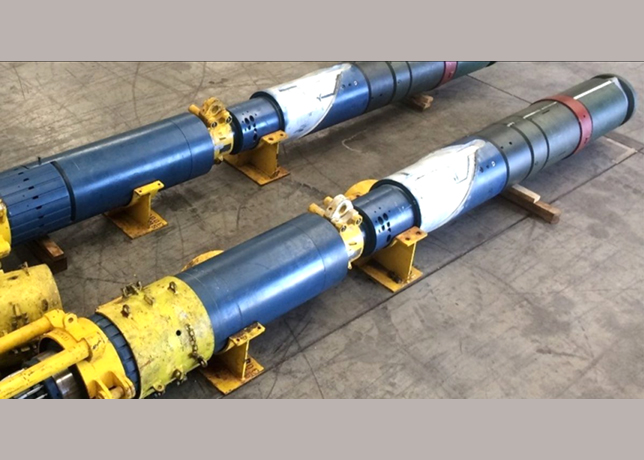
PE-RT is typically used for the straight lengths of pipe, providing a durable and flexible solution for extended sections. For more complex geometries and steel spools, ETFE is employed through a process known as roto-lining, which allows the material to evenly coat the internal surfaces of the steel spools.
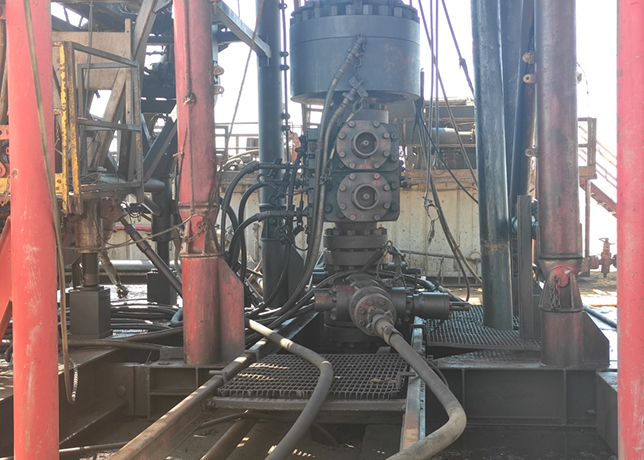
High-temperature resistant non-metallic liners, such as those made from PE-RT and ETFE, are used within existing steel piping networks to mitigate high-temperature corrosion and thermal degradation.
This practice extends the operational lifespan of steel pipes, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements.
Installation of non-metallic liners is also technically advantageous. These liners can be installed with minimal disruption to existing infrastructure, allowing for quick upgrades and reducing downtime.
The flexibility of PE-RT and the durability of ETFE facilitate installation in complex pipeline geometries and difficult-to-reach areas, which is particularly beneficial in offshore and remote locations common in the GCC.
The development of high-temperature resistant non-metallic liner pipes, specifically PE-RT and ETFE, represents a significant technical advancement in the materials used in the GCC's oil and gas sector.
These materials offer enhanced thermal stability and corrosion resistance, extending the life of steel piping networks and improving operational efficiency.
"As the GCC industry continues to innovate, the adoption of these advanced non-metallics is likely to expand, providing a robust technical solution to the challenges of modern pipeline management," says Braden Hwern, Marketing Manager, Muna Noor Manufacturing and Trading.