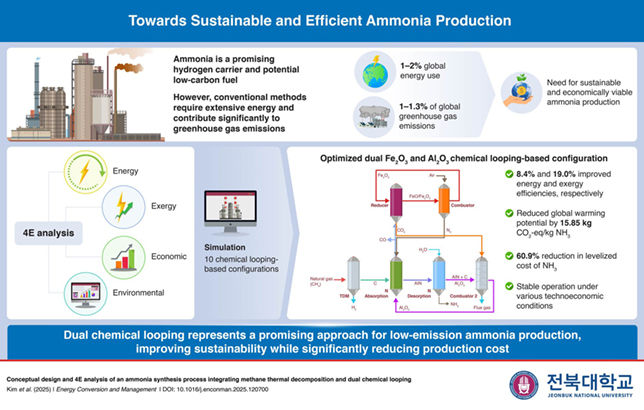
The segment has of late seen rapid adoption of modular processing, advanced treatment technologies, and industrial carbon capture innovations supported by rising LNG investment and market expansion
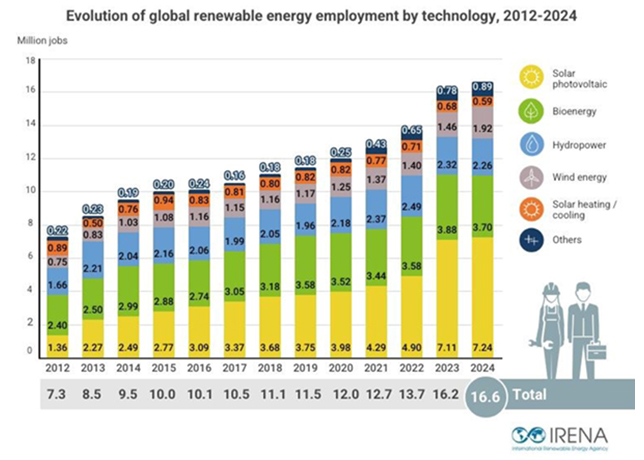
The segment has of late seen rapid adoption of modular processing, advanced treatment technologies, and industrial carbon capture innovations supported by rising LNG investment and market expansion
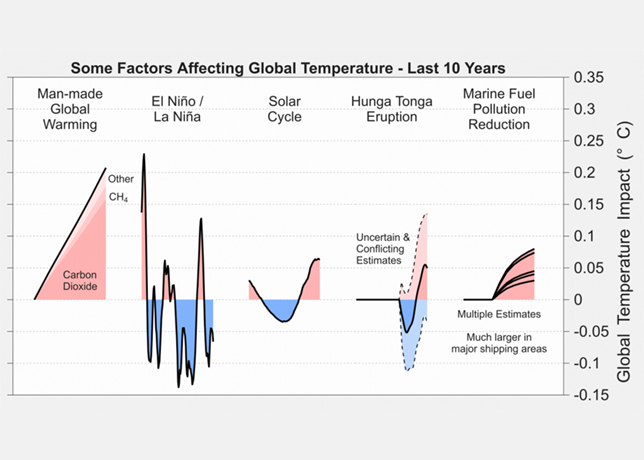
The segment has of late seen rapid adoption of modular processing, advanced treatment technologies, and industrial carbon capture innovations supported by rising LNG investment and market expansion
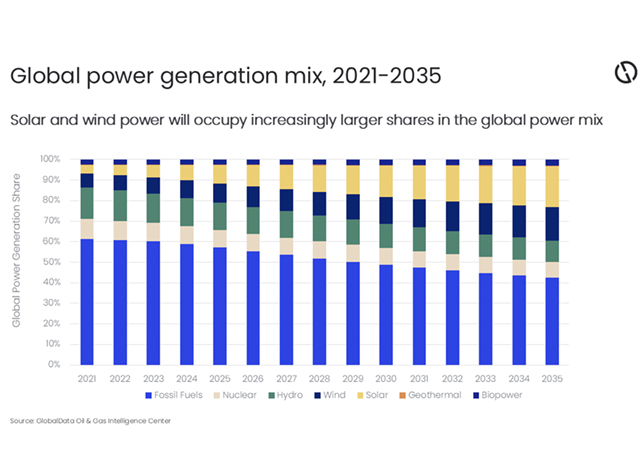
Natural gas processing and treatment has experienced a notable period of technological acceleration in the past six months, driven by industry imperatives to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, expand flexible infrastructure, and support a booming liquefied natural gas (LNG) export market.
Global LNG supply investment continued its strong trajectory in 2025, with more than 90 billion cu m per year of new liquefaction capacity reaching final investment decision, the second-highest annual total on record, reinforcing demand for processed and treated gas supplies.
North America accounted for over 80 billion cu m of this LNG capacity approvals, securing its role as the largest global LNG supplier.
This backdrop has clearly bolstered investment decisions in processing innovations and capacity expansions across key markets.
One of the most striking developments in gas processing technology has been the deployment of cutting-edge carbon capture and conversion technologies that go beyond traditional sweetening and dehydration improvements.
In January 2025, ADNOC Gas and Baker Hughes successfully installed British firm Levidian’s patented LOOP technology at the Habshan gas processing plant, marking the first deployment of a technology capable of capturing carbon from methane and converting it into graphene and hydrogen.
This unit is designed to produce more than one tonne per annum (tpa) of graphene and one tpa of hydrogen, with industrial-scale visions of up to 15 tpa in future iterations.
Data from this pilot will also support the refinement of associated AI modelling and digital twin technologies to reduce energy use and optimise outputs in future installations.
This dual-output approach represents a novel form of integration between gas processing and high-value product generation; transforming carbon management from a compliance cost to a potential revenue opportunity whilst also yielding low-carbon hydrogen that aligns with broader decarbonisation objectives.
The modularisation of gas processing plants has continued to gather momentum as companies seek to shorten deployment timelines, reduce capital intensity, and bring scalable processing units to remote and offshore fields.
Industry reports indicate that the global modular gas processing plant market is projected to grow from approximately $1.35 billion in 2025 to $1.45 billion in 2026, with an expected compound annual growth rate approaching 7.4 per cent through 2030.
Modular plants’ demand stems from their capacity for flexible configuration and faster construction compared to traditional large facilities, aligning with expanding unconventional gas production and LNG market demands.
On the treatment side of the value chain, technological advancements in purification and acid gas removal methods have been gathering pace.
Market research highlights accelerating innovation in membrane separation technologies and advanced adsorbents, which improve efficiency of H2S and CO2 removal, mitigate energy consumption, and support compliance with stricter pipeline gas quality standards.
These treatment innovations include next-generation membranes and adsorption media capable of handling high impurity loads while maintaining substantially higher selectivity and throughput compared with legacy treatment methods.
The commercial push toward such technologies is being driven by requirements for lower greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and tighter specifications in both pipeline and LNG export markets.
The broader gas treatment market is expected to grow steadily, increasing from an estimated $4.54 billion in 2025 to approximately $4.7 billion in 2026, with further growth forecast to $5.45 billion by 2030, reflecting longer-term expansion in natural gas throughput and more stringent environmental compliance regimes worldwide.
Infrastructure investments announced by midstream operators also illustrate developments in processing capacity and operational resilience in response to rising gas production volumes.
For example, Pembina Pipeline Corporation has advanced the Wapiti Expansion, which will increase processing capacity at its Wapiti plant by 115 million cu ft per day and has started on the construction of both processing and 28 MW cogeneration facilities to improve power resilience and lower operating costs. These projects are tracking on schedule for in-service dates in the first half of 2026.
Such projects underscore the growing trend of integrating power generation and processing infrastructure to achieve operational efficiencies and reduce dependency on external energy supplies.
Alongside hardware and process innovations, regulatory frameworks are also evolving.
Verra, a global carbon standard body, has released new certification modules (VMD0062 Capture from Natural Gas Processing, v1.0) designed to enable more accurate quantification of emission reductions from carbon capture activities at gas processing facilities, reflecting the growing intersections between market mechanisms, carbon accounting, and operational technology adoption.
The macroeconomic and investment context has also influenced decisions on gas processing expansions.
Despite macroeconomic headwinds and tighter margins across the broader oil and gas sector, emphasised by industry outlooks noting slower production growth alongside strategic technology adoption in 2025, key technological innovations have remained a priority for capital allocation in midstream operations.
The combined effect of these developments signals a meaningful shift in the natural gas processing and treatment landscape.
These innovations are not only enabling higher throughput and quality but also aligning the sector more closely with broader industrial decarbonisation goals and value chain diversification strategies.
In summary, the past six months have seen the industry pivot towards more flexible, decarbonised, and technologically advanced gas processing and treatment solutions, providing a foundation for continued growth in both traditional energy markets and emerging low-carbon applications.